Last update:
Physics news

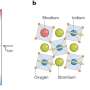
Beam balance designs could elucidate the origins of dark energy
One of the greatest problems in modern physics is to reconcile the enormous difference between the energy carried by random fluctuations in the vacuum of space, and the dark energy driving the universe's expansion.
General Physics
9 hours ago
2
82

Weird electron behavior gets even weirder: Charge fractionalization observed spectroscopically
A research team led by the Paul Scherrer Institute has spectroscopically observed the fractionalization of electronic charge in an iron-based metallic ferromagnet. Experimental observation of the phenomenon is not only of ...
Condensed Matter
13 hours ago
3
135

Designing a drone that uses adaptive invisibility: Towards autonomous sea-land-air cloaks
The idea of objects seamlessly disappearing, not just in controlled laboratory environments but also in real-world scenarios, has long captured the popular imagination. This concept epitomizes the trajectory of human civilization, ...
General Physics
12 hours ago
0
26

Photons that make quantum bits 'fly' for stable exchange of information in quantum computers
Two physicists at the University of Konstanz are developing a method that could enable the stable exchange of information in quantum computers. In the leading role: photons that make quantum bits "fly."
Optics & Photonics
13 hours ago
0
91

'Ruler for light' could enable detailed measurement in personal devices
Stanford researchers have unveiled a new type of frequency comb, a high-precision measurement device, that is innovatively small, ultra-energy efficient, and exceptionally accurate. With continued development, this breakthrough ...
Optics & Photonics
14 hours ago
0
11

Giant leap toward neuromorphic devices: High-performance spin-wave reservoir computing
A group of Tohoku University researchers has developed a theoretical model for a high-performance spin wave reservoir computing (RC) that utilizes spintronics technology. The breakthrough moves scientists closer to realizing ...
Condensed Matter
15 hours ago
0
11

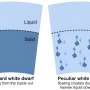
Researchers uncover new principle of motion in liquid crystals
A research team affiliated with UNIST has unveiled for the first time a new principle of motion in the microworld, where objects can move in a directed manner simply by changing their sizes periodically within a substance ...
Soft Matter
16 hours ago
0
111

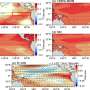
Study shows that the ATLAS detector can measure the flux of high-energy supernova neutrinos
High-energy neutrinos are extremely rare particles that have so far proved very difficult to detect. Fluxes of these rare particles were first detected by the IceCube Collaboration back in 2013.

Researchers develop method to manipulate structured light without distortion
The many properties of light allow it to be manipulated and used for applications that range from very sensitive measurements to communications and intelligent ways to interrogate objects. A compelling degree of freedom is ...
Optics & Photonics
Mar 5, 2024
0
129

New method measures the 3D position of individual atoms
For more than a decade it has been possible for physicists to accurately measure the location of individual atoms to a precision smaller than one-thousandth of a millimeter using a special type of microscope. However, this ...
Optics & Photonics
Mar 5, 2024
1
108

Shortcut to success: Toward fast and robust quantum control through accelerating adiabatic passage
In work published in Physical Review Letters researchers at Osaka University's Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research (SANKEN) used "the shortcuts to the adiabaticity (STA)" method to greatly speed-up the adiabatic ...
Condensed Matter
Mar 5, 2024
0
12

Open quantum system shows universal behavior
Universal behavior is a central property of phase transitions, which can be seen, for example, in magnets that are no longer magnetic above a certain temperature. A team of researchers from Kaiserslautern, Berlin and Hainan, ...
Quantum Physics
Mar 5, 2024
0
94

One way to improve a fusion reaction: Use weaknesses as strengths
In the Japanese art of Kintsugi, an artist takes the broken shards of a bowl and fuses them back together with gold to make a final product more beautiful than the original.
Condensed Matter
Mar 5, 2024
1
31

New soft magnetic materials for a high-frequency future
Imagine tiny magnets powering our world, silently switching energy on and off in phones, cars, and even power grids. These unsung heroes are called soft magnetic materials. However, as devices become faster and more efficient, ...
Condensed Matter
Mar 5, 2024
0
31

Scientists launch hub to channel quantum power for good
Scientists will work to channel the huge emerging power of quantum computers for the common good at a new institute that opened in Geneva on Tuesday, its founders said.
Quantum Physics
Mar 5, 2024
0
24

How scientists' ability to adapt led to new insights into magnetism
With time scheduled to use a certain beamline at the National Synchrotron Light Source-II (NSLS-II), scientists from NSLS-II and their partner institutions faced a challenge. They planned on researching a special type of ...
Condensed Matter
Mar 5, 2024
0
6

Tests show high-temperature superconducting magnets are ready for fusion
In the predawn hours of Sept. 5, 2021, engineers achieved a major milestone in the labs of MIT's Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC), when a new type of magnet, made from high-temperature superconducting material, achieved ...
Superconductivity
Mar 4, 2024
6
306
Gravity experiments on the kitchen table: Why a tiny, tiny measurement may be a big leap forward for physics
Just over a week ago, European physicists announced they had measured the strength of gravity on the smallest scale ever.
General Physics
Mar 4, 2024
4
139

Researchers find exception to 200-year-old scientific law governing heat transfer
A team of researchers led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst has recently found an exception to the 200-year-old law, known as Fourier's Law, that governs how heat diffuses through solid materials.
General Physics
Mar 4, 2024
0
129

Researchers use liquid crystals to control polarization inside laser-written waveguides
Researchers have developed a new way to control and manipulate optical signals by embedding a liquid crystal layer into waveguides created with direct laser writing. The new devices enable electro-optical control of polarization, ...
Optics & Photonics
Mar 4, 2024
0
83
More news
Plasma oscillations propel breakthroughs in fusion energy

Multiparticle nanostructures for building better quantum technologies

A key to the future of robots could be hiding in liquid crystals

LHCb observes a new decay mode of the charmed beauty meson

Beyond the ink: Painting with physics
Breaking an electrolyte's charge neutrality
New laser experiment spins light like a merry-go-round

Scientists make nanoparticles dance to unravel quantum limits

New maser in a 'shoebox' promises portable precision

Mass-produced, commercially-promising multicolored photochromic fiber
Scientists reveal how light behaves in formless solids

Better neutron mirrors can reveal the inner secrets of matter
Other news

Bumblebees surprise scientists with advanced social learning skills

Research reveals novel herpesvirus in South American pinnipeds

SpaceX eyes March 14 for next Starship test launch

Invasive plant time bombs: A hidden ecological threat

Not just humans: Bees and chimps can also pass on their skills

New deep-sea worm discovered at methane seep off Costa Rica

Genetic mutation in a quarter of all Labradors hard-wires them for obesity

Ultra-compact head-mounted fluorescence microscopes for neuroscience studies

A promising leap towards computers with light-speed capabilities
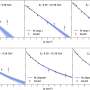
Study provides new insights into proton mass origins
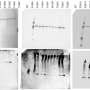
How insects tell different sugars apart
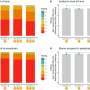
Standing together against hate: A collective responsibility

What makes birds so smart?