Last update:
Earth Sciences news

Geologists find that low-relief mountain ranges are the largest carbon sinks
For many hundreds of millions of years, the average temperature at the surface of the Earth has varied by not much more than 20° Celsius, facilitating life on our planet. To maintain such stable temperatures, Earth must ...
Earth Sciences
1 hour ago
0
2

Soil may release more carbon than expected, affecting climate change models
The accuracy of climate models depends on many factors—greenhouse gas emissions from industrial and transportation activity, farm animal "emissions," urban growth and loss of forests, and solar reflections off snow and ...
Earth Sciences
2 hours ago
0
29

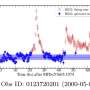
New research shakes up what we knew about Idaho's big 2020 earthquake that hit Boise
New research is shaking up what we know about Idaho earthquakes and the faults that cause them as scientists try to better understand the state's seismic activity.
Earth Sciences
3 hours ago
0
5

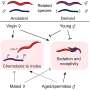
Nearly 2 billion people globally at risk from land subsidence
Land subsidence is a geohazard caused by the sudden or gradual settling (years to decades) of the land surface due to the removal of subsurface material. This can be due to a variety of factors, both natural (such as earthquakes, ...

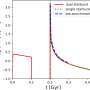
Deadly earthquakes trigger hunt for speedier alerts
Researchers in Europe have identified an underground signal that may be a precursor to strong quakes.
Earth Sciences
5 hours ago
0
15

Deep sea and sediments bring iron to Antarctic waters, finds researcher
Deep sea and sediments bring iron to Antarctic waters. The iron that fertilizes the waters around Antarctica mostly comes from the deep, upwelling waters and the sediments around the continent.
Earth Sciences
23 hours ago
0
34

Comparable net radiation between the high-elevation Tibetan Plateau and the low-elevation Yangtze River region: Study
Land–atmosphere interactions play a crucial role in shaping Earth's climate system, profoundly influencing weather patterns, climate variables, and ecological processes. Despite being located at similar latitudes, the Tibetan ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
19

Understanding wind and water at the equator are key to more accurate future climate projections: Study
Getting climate models to mimic real-time observations when it comes to warming is critical—small discrepancies can lead to misunderstandings about the rate of global warming as the climate changes. A new study from North ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
222

Q&A: A cutting-edge methane monitor
After more than seven years of development, MethaneSAT recently launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. A collaboration between the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard-Smithsonian ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
2

Frozen in time: Old paintings and new photographs reveal some NZ glaciers may soon be extinct
As the austral summer draws to a close, we are preparing to fly over the Southern Alps to survey glaciers. This annual flight supports the longest scientific study of Aotearoa New Zealand's icescapes—and it shows that all ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
5

Researchers provide unprecedented view into aerosol formation in Earth's lower atmosphere
Eighty-five percent of the Earth's air resides in the lowest layer of its atmosphere, or troposphere. Yet, major gaps remain in our understanding of the atmospheric chemistry that drives changes in the troposphere's composition.
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
2

Ever heard of the Maritime Continent? It's not far from Australia—and channels heat around the world
Africa, Asia, Australia, Antarctica, North and South America, Europe—and the Maritime Continent.
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
3

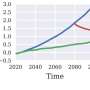
Study suggests sinking land increases risk for thousands of coastal residents by 2050
One in 50 people living in two dozen coastal cities in the United States could experience significant flooding by 2050, according to Virginia Tech-led research.
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
38

Ice cores suggest 16th-century pandemics may have caused declines in atmospheric CO₂
Changes in human activity may have led to atmospheric CO2 levels declining in the 16th century, due to large-scale land use changes in the Americas during New World-Old World contact between 1450 and 1700 CE, suggests a Nature ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 6, 2024
0
1

Satellite catches coastal flooding during California storms
A series of atmospheric rivers drenched California in February, with record amounts of rainfall and hurricane-force winds sweeping across parts of the state. At one point, weather agencies posted flood watches for nearly ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 5, 2024
0
6

How does a river breathe? The answer could lead to a better understanding of the global carbon cycle
Take a deep breath. Pay attention to how air moves from your nose to your throat before filling your lungs with oxygen. As you exhale your breath, a mix of oxygen and carbon dioxide leaves your nose and mouth.
Earth Sciences
Mar 5, 2024
0
30

After decades of Arctic sea ice getting faster, models suggest a dramatic reversal is coming
Will ice floating in the Arctic Ocean move faster or slower over the coming decades? The answer to this question will tell us whether marine transportation can be expected to get more or less hazardous. It might also have ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 5, 2024
0
137

We know the Arctic is warming—what will changing river flows do to its environment?
Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently combined satellite data, field observations, and sophisticated numerical modeling to paint a picture of how 22.45 million square kilometers of the Arctic will ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 5, 2024
0
287

In a dangerously warming world, the grim reality of Australia's bushfire emissions must be confronted
In the four years since the Black Summer bushfires, Australia has become more focused on how best to prepare for, fight and recover from these traumatic events. But one issue has largely flown under the radar: how the emissions ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 5, 2024
0
10

Global warming may be behind an increase in the frequency and intensity of cold spells
Global warming caused by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases is already affecting our lives. Scorching summers, more intense heat waves, longer drought periods, more extended floods, and wilder wildfires are consequences ...
Earth Sciences
Mar 5, 2024
0
6
More news

The lows and lows of Antarctic sea ice

Hidden 'star' sand dune mystery solved by ancient find

Antarctica's coasts are becoming less icy, researchers find
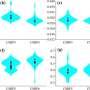
Scientists sort out uncertainties in sea level projections
Other news

AI makes a rendezvous in space

New technique may help scientists stave off coral reef collapse

Vitamin A may play a central role in stem cell biology and wound repair
Often seen, never studied: First characterization of a key postsynaptic protein

Earth's earliest forest revealed in Somerset fossils

NASA's network of small moon-bound rovers is ready to roll
Scientists develop new machine learning method for modeling chemical reactions
What makes a pathogen antibiotic-resistant?

Dancing droplets' new spin on water harvesting