This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Scientists 'break the mold' by creating new colors of blue cheese
Experts at the University of Nottingham have discovered how to create different colors of blue cheese. After discovering how the classic blue-green veining is created, a team of experts from the School of Life Sciences, were able to create a variety of different fungal strains that could be used to make cheese with colors ranging from white to yellow-green to red-brown-pink and light and dark blues.
The findings of the study are published in the journal npj Science of Food.
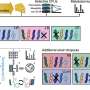
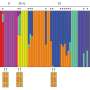
The fungus Penicillium roqueforti is used worldwide in the production of blue-veined cheese such as Stilton, Roquefort and Gorgonzola. Its unique blue-green color and flavor comes from pigmented spores formed by fungal growth. Using a combination of bioinformatics, targeted gene deletions and heterologous gene expression, the research team, led by Dr. Paul Dyer, Professor of Fungal Biology, learned the way in which the blue-green pigment is produced.
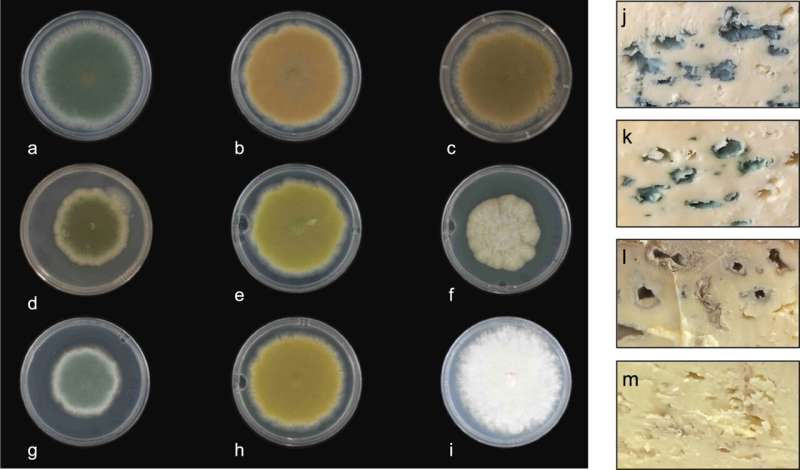
The researchers found that a biochemical pathway gradually forms the blue pigments, starting at a white color, which progressively becomes yellow-green, red-brown-pink, dark brown, light blue, and finally dark blue-green. The team were then able to use some classic food safe (non GM) techniques to "block" the pathway at certain points, and so create strains with new colors that can be used in cheese production.
Dr. Dyer said, "We've been interested in cheese fungi for over 10 years and traditionally when you develop mold-ripened cheeses, you get blue cheeses such as Stilton, Roquefort and Gorgonzola which use fixed strains of fungi that are blue-green in color. We wanted to see if we could develop new strains with new flavors and appearances.
"The way we went about that was to induce sexual reproduction in the fungus, so for the first time we were able to generate a wide range of strains which had novel flavors including attractive new mild and intense tastes. We then made new color versions of some of these novel strains."
Once the team produced the cheese with the new color strains, they then used lab diagnostic instruments to see what the flavor might be like.
"We found that the taste was very similar to the original blue strains from which they were derived," said Dr. Dyer. "There were subtle differences but not very much.
"The interesting part was that once we went on to make some cheese, we then did some taste trials with volunteers from across the wider University, and we found that when people were trying the lighter-colored strains they thought they tasted more mild. Whereas they thought the darker strain had a more intense flavor.
"Similarly, with the more reddish brown and a light green one, people thought they had a fruity tangy element to them—whereas according to the lab instruments they were very similar in flavor. This shows that people do perceive taste not only from what they taste but also by what they see."
The team, which included lead postgraduate student Matt Cleere, will now look at working with cheese makers in both Nottinghamshire and Scotland to create the new color variants of blue cheese. A University spin-out company called Myconeos has also already been established to see if the strains can be commercialized.
"Personally, I think it will give people a really satisfying sensorial feeling eating these new cheeses and hopefully might attract some new people into the market," adds Dr. Dyer.
More information: Matthew M. Cleere et al, New colours for old in the blue-cheese fungus Penicillium roqueforti, npj Science of Food (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41538-023-00244-9
Provided by University of Nottingham