This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
High-severity wildfires threaten global timber production, new study finds
Severe wildfires are putting global timber production at risk, new research from The Australian National University (ANU), the University of Sheffield and the University of Cambridge shows.
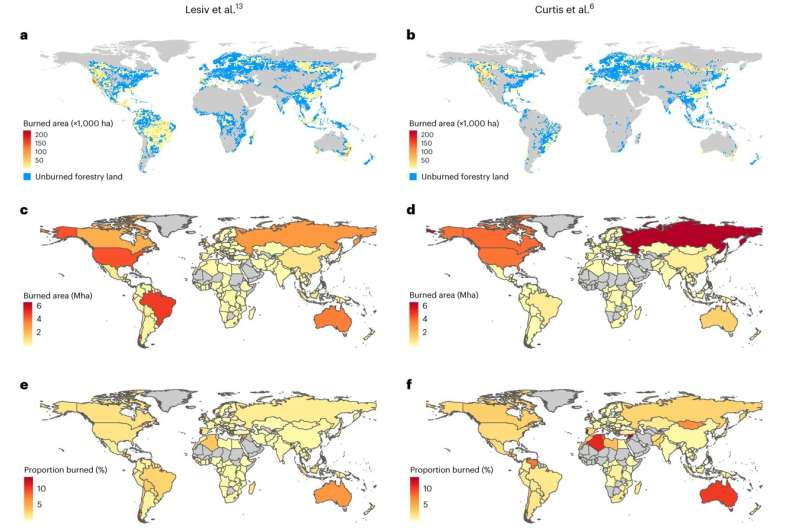
The research team analyzed data from 2001 to 2021 and found 18.5 to 24.7 million hectares of timber-producing forest, an area equivalent to the size of Great Britain, has been lost to wildfires across the globe in the last two decades.
The researchers warn wildfires caused a loss of approximately 393 to 667 million cubic meters of industrial timber worth $45 to 77 billion based on 2021 global export prices. The findings are published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
According to lead author Dr. Chris Bousfield from the University of Sheffield, the regions most severely impacted include Australia, the western United States of America and Canada, Siberian Russia and Brazil.
"Countries such as Australia, who have already lost a large proportion of their total timber-producing forests this century, are now likely to see significant shortfalls in their domestic timber supply," Dr. Bousfiled said.
"This begs the question of where the additional timber needed to meet demand will be sourced from, and at what cost to the environment."
Co-author Professor David Lindenmayer from ANU and the Biodiversity Council said, "What's particularly concerning is the discernible and relentless upward trajectory in annual burned areas—a clear sign of the growing wildfire-induced losses anticipated due to severe climate change.
"As we strive to meet the ever-increasing demand for timber, it is clear that timber producers must urgently adapt by adopting innovative management strategies and new technology to counter the escalating threat posed by wildfires."
The researchers argue governments and industry must do four things to secure future timber production.
- Expand timber production through fast-growing plantations of less-flammable tree species.
- Establish plantations in regions that are less likely to burn.
- Better design plantations to reduce fire spread across landscapes and damage and risk to human communities.
- Embrace emerging technologies such as infrared-sensing drones and autonomous firefighting systems to enhance wildfire detection and suppression.
"Failure to implement these approaches could lead to significant future timber losses, potentially resulting in higher timber prices," senior author Professor David Edwards from Cambridge University said.
"This, in turn, may increase the economic attractiveness of intensive logging in some tropical forests, posing a threat to conservation efforts in biodiversity hotspots."
More information: Christopher G. Bousfield et al, Substantial and increasing global losses of timber-producing forest due to wildfires, Nature Geoscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01323-y
Journal information: Nature Geoscience
Provided by Australian National University