This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Unveiling the wonders of ciliate conjugation: Insights from Paramecium jenningsi
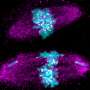
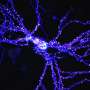
Ciliate protozoa possess the remarkable ability to reproduce through both asexual and sexual means. Their distinctive sexual process involves conjugation and autogamy, and they wield a secret weapon: extraordinary nuclear dimorphism. Within each cell resides both a germline micronucleus (MIC) and a somatic macronucleus (MAC). When subjected to fluorescent staining, their sexual processes transform into a captivating kaleidoscope of vibrant colors, creating a cellular carnival of vibrant colors.
To investigate these processes in closely related species, an international team of researchers focused on Paramecium jenningsi, a relative within P. aurelia complex (a star in the cellular cosmos).
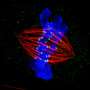
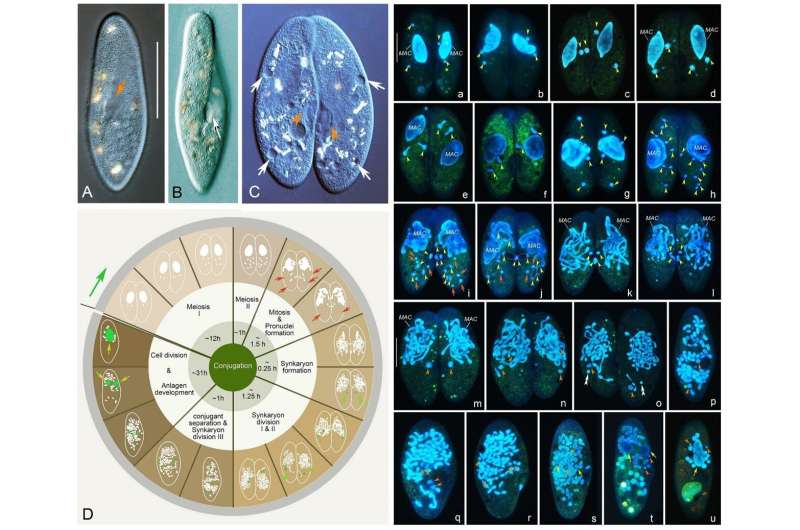
The team found that in P. jenningsi, the conjugation process unfolds over approximately 48 hours, encompassing three prezygotic divisions (meiosis I, II, and mitosis) and three postzygotic divisions. Notably, during this process, the MICs are predominantly characterized by the "parachute" phase occurring at the prophase of meiosis I.
"Following meiosis II, a variable number of nuclei undergo the third prezygotic division. The two resulting products near the paroral cone subsequently evolve into the genetically identical migratory and stationary pronuclei," shared the study's co-first author Ruitao Gong.
Further, the synkaryon, formed during conjugation, undergoes three divisions, giving rise to the MIC and MAC anlagen. Interestingly, only one nuclear product from the first postzygotic division proceeds to complete the subsequent two divisions.
"An additional cell division becomes necessary to finalize the last phase of conjugation. During this step, two MIC anlagen undergo mitotic division, while two MAC anlagen are distributed between the daughter cells without division," added Xue Zhang, the other co-first author.
This study, published in Water Biology and Security, provides a new model ciliate for further investigation of nuclear selection and differentiation, as well as nuclear morphology during meiosis.
"The process of conjugation in ciliates is truly remarkable. In fact, in other species, we have observed that individuals lacking micronuclei can also engage in conjugation," said Zhang.
More information: Xue Zhang et al, Nuclear events during conjugation in the poorly studied model ciliate Paramecium jenningsi, Water Biology and Security (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.watbs.2023.100201
Provided by KeAi Communications Co.