This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Residents unprepared for wildland fires, face barriers in implementing prevention measures: Study
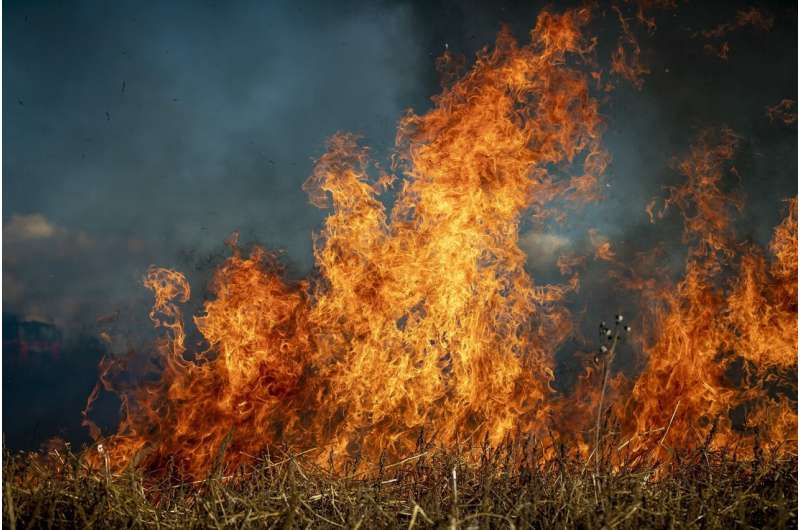

This year, Canada saw the worst wildfire season in its history, with fires destroying homes, displacing thousands of residents, and burning the largest area since contemporary records began in 1983. Much of this damage to communities could be reduced with better wildfire preparedness—but wildland urban interface (WUI) communities often face significant barriers in implementing these improvements, according to a study by York University's Disaster and Emergency Management researchers.
According to the study, Determinants of residential wildfire mitigation uptake: A scoping review, 2013–2022, published in the Fire Safety Journal, there are many residential wildfire mitigation and educational programs to protect residential communities from wildfires and to help prevent related disasters.
"Unfortunately, knowing how to protect and mitigate the risk to WUI communities from wildfire is not sufficient," says Professor Eric B. Kennedy in the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Professional Studies, who co-authored the study. "Understanding what will lead to adoption of prevention measures is a high-priority issue to better prepare for future wildfire seasons."
These kinds of studies—known as scoping reviews—help to identify patterns and consensus in scientific research. Kennedy's co-author and York graduate Sarah Cowan presented the results today at the 14th International Symposium on Fire Safety Science, IAFSS2023, held in Tsukuba, Japan. She highlighted that based on their review of 78 academic journal articles published in the last decade, several individual and social factors that contribute to a lack of preparedness were identified.
"We found a number of things that might help to increase wildfire preparedness. For example, many studies that we reviewed documented how the lack of money, time, resources or physical ability can impair the ability to make improvements to a property," highlights wildfires researcher Kennedy.
"For instance, many of the home improvements can be expensive, and if you don't have the money, financial support, or even support from your insurance company with incorporating improvements during rebuilding, it can be really challenging to make a difference. Same thing if we have an aging population. Cutting back vegetation or emptying and cleaning your eavestroughs can be physically demanding."
The authors saw a pattern in how some residential organizations can negatively impact wildlife preparedness.
"Studies also showed that rules and norms set by some homeowners' associations can sometimes make properties more vulnerable and more likely to burn," says Kennedy. "For instance, if they were trying to preserve certain aesthetics, they might use materials that burn more easily or capture embers from nearby fires."
He adds that homeowners' associations and municipalities should ensure building codes are in line with best practices to prevent such disasters.
"There really is an opportunity to broaden out the locations where these studies are being done. We need more research with more communities to help us understand how to develop solutions that can work across diverse contexts," Kennedy observes.
The authors also note that a majority of the studies on this topic have been done in Australia, Canada and the US.
More information: Sarah Cowan et al, Determinants of residential wildfire mitigation uptake: A scoping review, 2013–2022, Fire Safety Journal (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2023.103851
Provided by York University