This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Are pulsars the key to finding dark matter?

Ah, dark matter particles, what could you be? The answer still eludes us, and astronomers keep trying new ideas to find them. A new paper in Physical Review Letters suggests that if dark matter is made of axions, we might see their remnant glow near pulsars.
While the most popular candidate particles for dark matter are weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs), another popular option is the hypothetical axion. Axions weren't originally proposed to solve dark matter, but rather to address some vexing subtleties in particle physics. [Fun fact: Axion is a brand of dishwashing liquid popular in Latin America. Axions are so named because they "clean up" the particle physics problem.]
According to theory, axions are low-mass, chargeless particles that wouldn't interact strongly with regular matter or light, which sounds like a perfect dark matter candidate. Axions can decay into photons, but the light produced would be so diffuse and faint that we can't detect it.
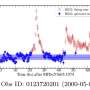
This new study proposes a way we might be able to detect the remnant glow of axions. If they exist, axions could be produced in extremely strong magnetic fields, such as those around neutron stars and black holes. The strongest electromagnetic fields are around pulsars, so that would be the best place to look. Pulsars are neutron stars that generate powerful streams of energy from their magnetic poles. The polar regions would also produce vast quantities of axions, some of which would decay into light. So in theory pulsar light should contain the light of axion decay.
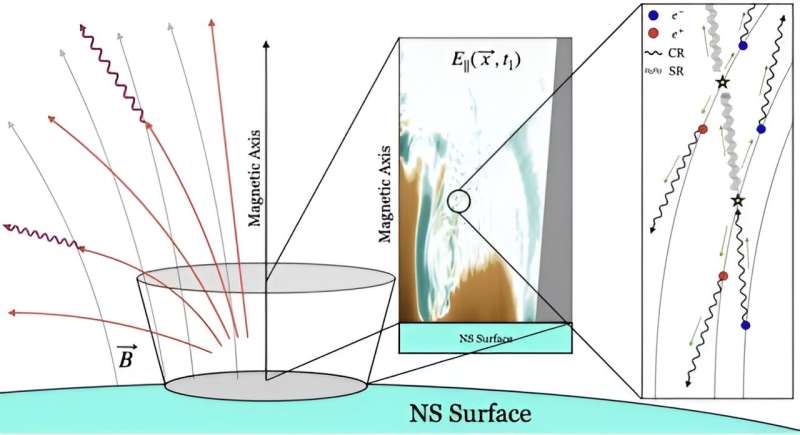
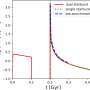
So the authors used a basic model to estimate the amount of light that would be produced by axion decay and what the spectrum of that light would be. They then simulated how this excess would appear in the radio flashes of powerful pulsars. They then compared their model to observations of 27 nearby pulsars to see if they could detect an excess of radio light that would prove axion decay.
Unfortunately, the team found no evidence for axions. Based on their observations, they were able to constrain the mass of axions if they do exist. Based on the data, axions can be no lighter than 10-8 electron volts and no heavier than 10-5 electron volts, which is much lighter than even neutrinos.
One of the strengths of this result is that it doesn't assume axions are dark matter, only that axions exist. This is really more of a particle physics test than a cosmological one, which is why the mass constraint can be so direct. But once again the particles of dark matter remain hidden. Assuming dark matter particles exist, which is a story for another time.
More information: Dion Noordhuis et al, Novel Constraints on Axions Produced in Pulsar Polar-Cap Cascades, Physical Review Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.111004
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by Universe Today