This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Virgin Galactic notches fourth spaceflight in four months
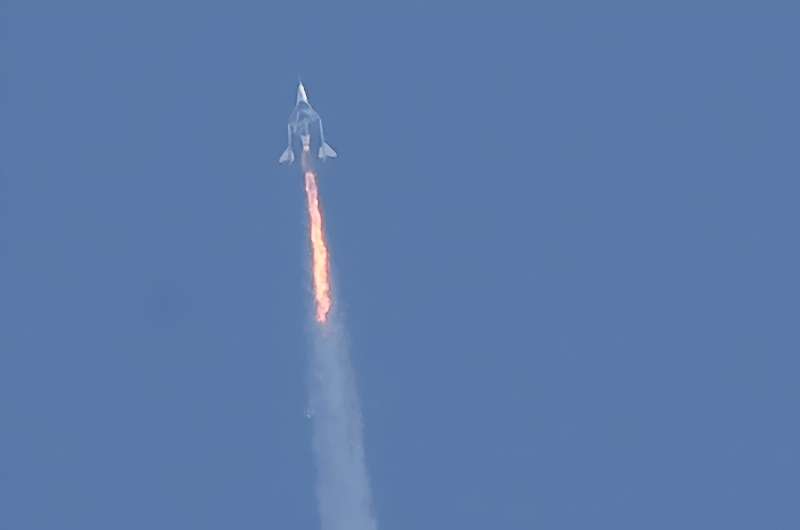

Virgin Galactic on Friday announced it had sent three paying customers on an hour-long journey to space and back, racking up its fourth successful flight in as many months.
The private astronauts aboard the Galactic 03 mission were among the first people to buy their tickets from the company founded by British billionaire Richard Branson in 2004.
American real estate entrepreneur Ken Baxter, South Africa-born conservationist Timothy Nash, and British engineer and entrepreneur Adrian Reynard took their places aboard the rocket-powered spaceplane VSS Unity, along with Virgin Galactic's astronaut instructor Beth Moses.
"What a thrilling day for our three new private astronauts and the entire team at Virgin Galactic," said CEO Michael Colglazier.
The spaceflights involve a giant, twin-fuselage carrier aircraft with two pilots that takes off from a runway at Spaceport in New Mexico.
This mothership, called VSS Eve, gains a high altitude then drops the spaceplane attached below it, which in turn engages its thrusters to soar into space at speeds approaching Mach-3.
Passengers experience a few minutes of weightlessness, where they are free to perform somersaults and gaze out the window at the curvature of the Earth.
The company's first private mission in June involved members of the Italian Air Force, and was followed in August by the launch of its first tourists, including a mother-daughter pair who won their spots in through a sweepstakes competition for charity.
Friday's flight launched at 8:34 am Mountain Time (1434 GMT) and landed at 9:36 am (1536 GMT), with VSS Unity achieving a maximum altitude of 55 miles (89 kilometers).
In a notable first, Nash brought with him two fossils of human ancestors to space, "the clavicle (collar bone) of the almost 2-million-year-old Australopithecus sediba and a thumb bone of Homo naledi, dated to about 250,000 years ago," according to Virgin Galactic's website.
Both were discovered in the Cradle of Humankind, a UNESCO World Heritage Site near Johannesburg in South Africa.
Virgin Galactic competes in the "suborbital" space tourism sector with billionaire Jeff Bezos's company Blue Origin, which has already sent 31 people into space using a vertical lift-off rocket.
But since an accident in September 2022 during an unmanned flight, Blue Origin's rocket has been grounded. The company promised in March to resume spaceflight soon.
Virgin Galactic meanwhile plans to press ahead with monthly commercial spaceflights. It has sold around 800 tickets—600 between 2005 and 2014 for $200,000 to $250,000, and 200 since then for $450,000 each.
© 2023 AFP