This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New study reveals global patterns in marine fish body size and trophic traits with latitude and depth
Just published in PeerJ Life & Environment, a new research article by Professor Mark Costello (Nord University) and Doctor Han-Yang Lin (University of Auckland) unveils a comprehensive analysis of the relationships between body size, trophic level (position in the food web), latitude, and depth for marine fish species on a global scale. The study sheds light on the complex interplay between evolutionary characteristics and environmental factors in shaping the functional traits of marine species.
"Body size and trophic level increase with latitude, and decrease in the deep-sea and Antarctica, for marine fish species" delves into the intricate dynamics governing the functional traits of marine fish species across latitudinal and depth gradients.
Traditionally, three main theories—the temperature-size rule (TSR), gill-oxygen limitation theory (GOLT), and temperature constraint hypothesis (TCH)—have been proposed to explain the variations in body size and trophic levels of marine species. Until now, however, no study has quantified the relationship between functional traits, latitude, and depth on a global scale for any marine taxon.
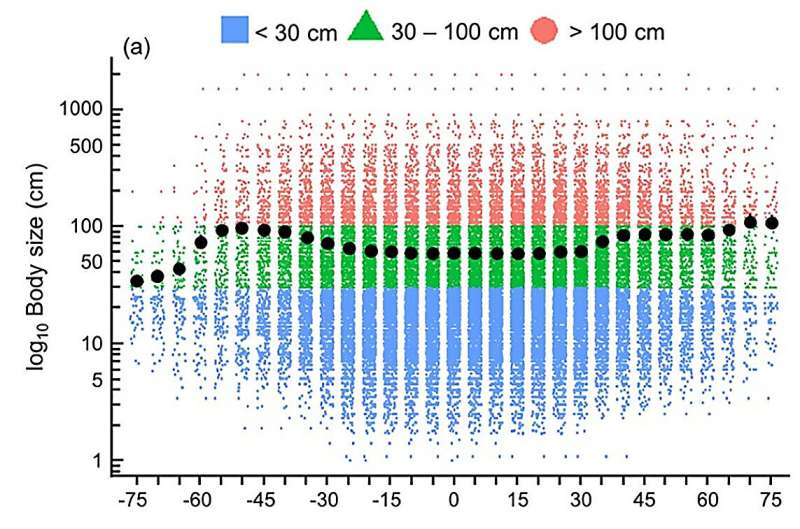
Through an extensive analysis of 5,619 marine fish species, the researchers compared the latitudinal gradients of maximum body size and trophic level within different depth zones, including the whole water column and various depth intervals. The study revealed compelling patterns: marine fish species tend to exhibit larger body sizes and higher trophic levels in high latitudes, while the opposite is observed in warmer latitudes, except for the Southern Ocean (Antarctica).
The researchers attribute these disparities to the contrasting environmental heterogeneity between the Arctic and Antarctica. The more variable Arctic conditions host a wider diversity of fish species in terms of body size and trophic level.
Furthermore, the study highlights the dominance of fish species with trophic levels ≤ 2.80 in warmer environments, whereas these species are absent in colder regions.
This finding underscores the role of temperature in shaping the composition of marine fish communities. Intriguingly, the study also identified a decline in mean maximum body size of fish species with increasing depth, which is attributed to reduced dissolved oxygen levels. This observation aligns with the TSR, GOLT, and TCH hypotheses, providing further validation for these theories.
"What I found most remarkable was the contrast between the two polar regions because they are often considered comparable, but the Arctic and Antarctic are not in terms of environmental variability and biodiversity. Also, while average species body size generally got larger in colder (high latitude) temperatures this was not the case in the deep sea, probably due to food and/or oxygen limitations," stated Professor Mark Costello.
The findings of this study have far-reaching implications for marine ecology and our understanding of how various factors shape the distribution and traits of marine organisms. As the first global-scale quantification of functional trait variations for a marine taxon, this research lays the foundation for more targeted conservation efforts and deeper exploration of the mechanisms governing marine biodiversity.
More information: Han-Yang Lin et al, Body size and trophic level increase with latitude, and decrease in the deep-sea and Antarctica, for marine fish species, PeerJ Life & Environment (2023). DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15880
Provided by PeerJ