This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New leaf-tailed gecko from Madagascar is a master of disguise

Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of camouflage. Some species have skin flaps around the whole body and head, as well as flattened tails. During the day, they rest head-down on tree trunks with these skin flaps spread out, and blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them nearly impossible to spot. At night, they awaken to prowl the fine branches of the understory looking for invertebrate prey.
"When we first discovered this species in 2000, we already suspected it might be new to science," says Dr. Frank Glaw, curator of herpetology at the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology, lead author on the study. "But it has taken us many years to amass enough information to confidently describe it as a new species."
The team collected data on the genetics, morphology, and the distribution of the species. Several expeditions to northern Madagascar were undertaken that expanded knowledge of this new species. The discovery was announced on August 15 in Salamandra.
-

Leaf-tailed geckos are good jumpers, and often bring their hands and feet together before leaping. Credit: Dr. Jörn Köhler, Hessisches Landesmuseum Darmstadt, Germany -
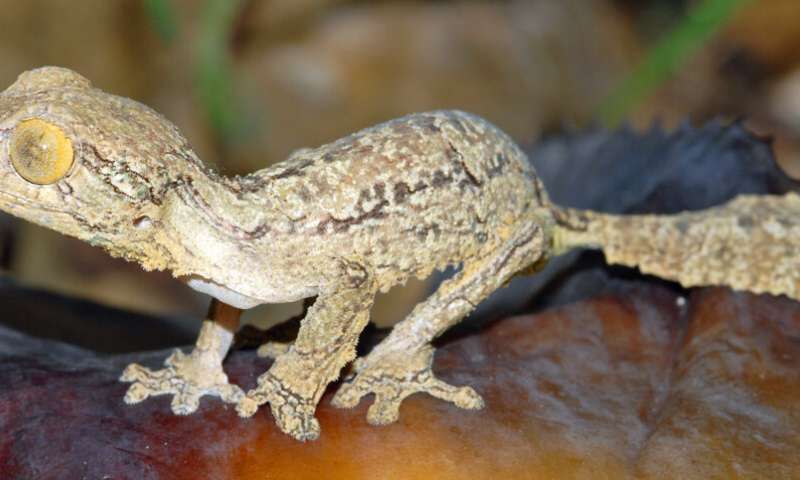

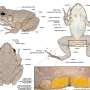
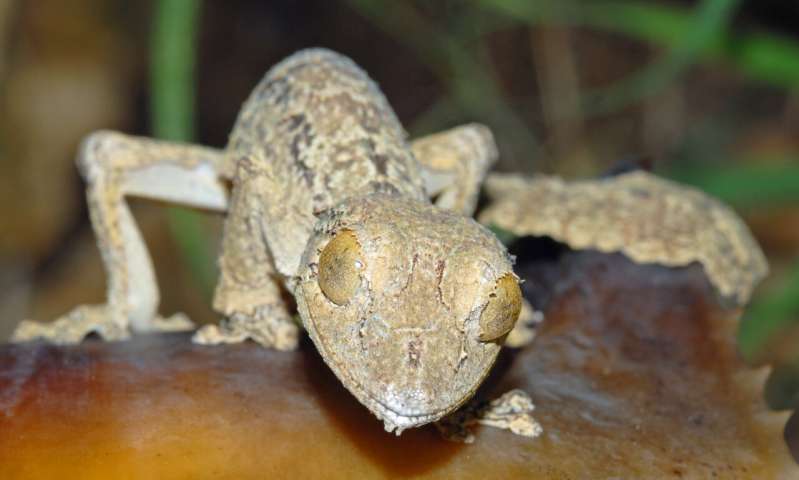
The unusual eyes of Uroplatus garamaso help to distinguish it from closely related species of leaf-tailed geckos. Credit: Dr. Jörn Köhler, Hessisches Landesmuseum Darmstadt, Germany
One challenge was that Uroplatus garamaso is remarkably similar to another species, Uroplatus henkeli, and has been confused with it in the past. "This is quite common for reptiles from Madagascar," explains Dr. Jörn Köhler of the Hessisches Landesmuseum Darmstadt. "There are a lot of these so-called 'cryptic species,' which are waiting for taxonomic treatment."
By careful analysis, the authors were able to find some features that differentiate the two species. "The real key was the discovery that the tip of the tongue is blackish in U. henkeli, whereas it is pink in U. garamaso," says Dr. Philip-Sebastian Gehring of the University of Bielefeld, Germany. At 20 cm long, the new species is also a little smaller than U. henkeli, and has a narrower tail.
"The new species is the latest in a series of new Uroplatus geckos described from Madagascar over the last few years," says Dr. Fanomezana Ratsoavina of the University of Antananarivo, Madagascar, who did her Ph.D. on leaf-tailed geckos.
-
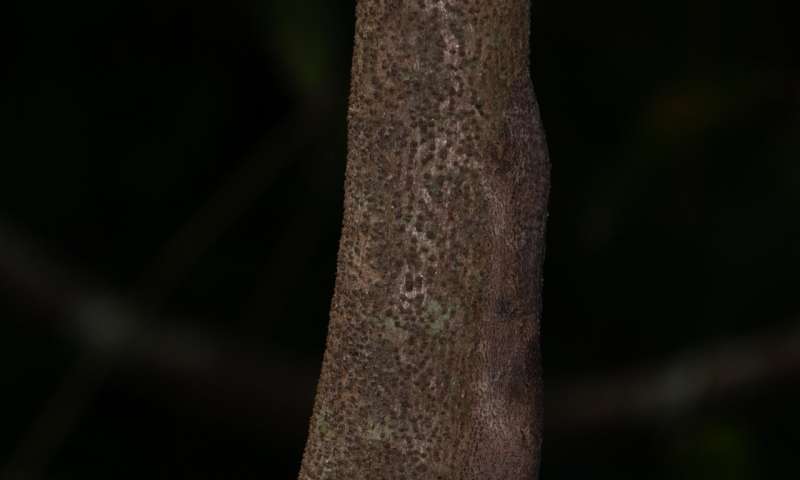

Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of disguise, and Uroplatus garamaso is one of the best. Here, the gecko is hiding on the right hand side of the tree trunk. Credit: Dr. Mark D. Scherz, Natural History Museum of Denmark -
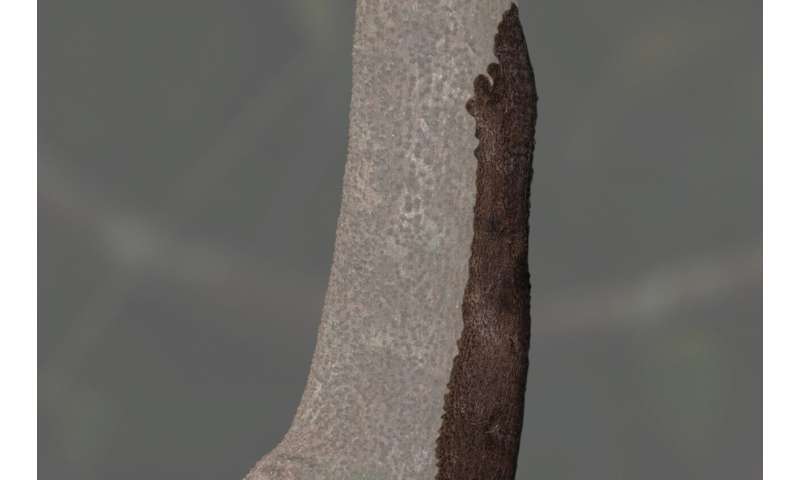

Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of disguise, and Uroplatus garamaso is one of the best. Here, we reveal the gecko in its hidden position. Credit: Dr. Mark D. Scherz, Natural History Museum of Denmark -
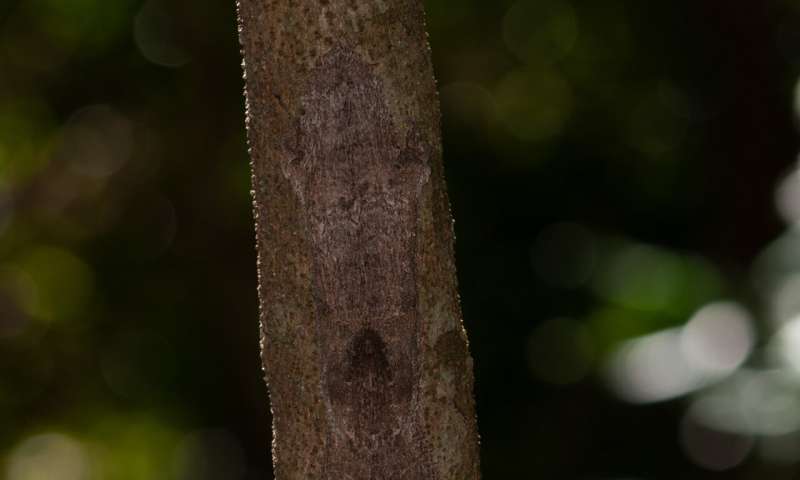

During the day, Uroplatus garamaso rest hidden, head-down on tree trunks, with their hindlimbs outstretched and fringes pressed against the bark, making them almost impossible to spot. Here, the gecko is viewed straight on, as one might (not) find them in the forest. Credit: Dr. Mark D. Scherz, Natural History Museum of Denmark
"We are close to completing the taxonomic inventory of the genus, but this is just the start of our understanding of their evolution and ecology," says Dr. Mark Scherz, curator of herpetology at the Natural History Museum of Denmark.
"The mouth color, which has been so useful to identify different species, has a totally unknown function. There is a lot we still do not know about these geckos, from their broader evolutionary relationships to their behavior."
More information: Frank Glaw et al, A new large-sized species of leaf-tailed gecko (Uroplatus) from northern Madagascar, Salamandra (2023).
Provided by University of Copenhagen