This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
Crowd-sourced science sheds light on how new species form across space and time

Imagine a jungle. It's probably a lush forest, filled with different bird songs and the hum of thousands of different kinds of insects. Now imagine a tundra: barren, windswept terrain with relatively few kinds of plants or animals.
These two places highlight an interesting phenomenon—that some places on Earth have far more species than others. In fact, the distribution of species across the globe follows a curiously consistent pattern: generally, there are more species closer to the equator and fewer as you move towards the poles. This "latitudinal biodiversity gradient" can be observed across many different groups of organisms over time.
One possible explanation for the presence of more species closer to the equator is that changes in climate from the equator to the poles affects the ability of new species to evolve—a process called speciation.
Diversity in action
Our research team at the University of British Columbia turned to unique tools and species to track exactly how climate influences evolution, and what this means for where new species appear. And we conducted this research while we were stuck at home during COVID-19 lockdowns. Our research is now published in PLOS ONE.
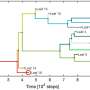
The fall webworm is a moth found from Mexico to Canada (a range of almost 4,000 km) whose caterpillars have either black or red heads. While this might seem like a subtle difference, caterpillars with these different colors seem to have different behaviors and appear at different times of the year, and genetic studies suggest that they are evolving into different species.
This moth is also found throughout vastly different climates, which allowed us to explore how latitude and climate might be affecting their ability to turn from one species into two.
However, we had a problem: with global lockdowns and travel restrictions, we couldn't even leave our homes, much less sample caterpillars across an entire continent. So, we turned to crowd-sourced science. Some apps and websites use user-uploaded photos or audio clips to identify flora and fauna, creating huge databases of nature observations.
Thanks to backyard observers, we could access thousands of observations across North America from the comfort of our homes to begin investigating speciation on a large geographic scale.
Birth of new species
The process of speciation occurs when two groups of organisms belonging to the same species are separated by a barrier that prevents them from reproducing. The most well-known way that this can occur is through a physical barrier between the groups, like a mountain range or a highway.
For the fall webworm, the barrier causing them to become two different species is time. In general, moth species only appear and reproduce during the summer, and when they do, they breed for only a few weeks, at most.
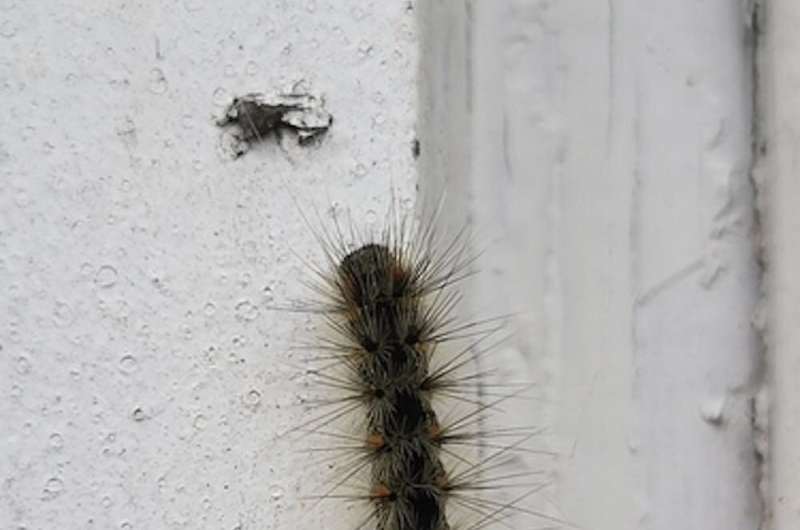

The red-headed and the black-headed fall webworms tend to emerge and reproduce at different times during the summer, and this time gap creates a barrier that is causing them to become two different species.
Summers toward the equator tend to be much longer, so the fall webworms go through more life cycles in a year compared to northern populations, which are only able to breed once during short summers. If the red-headed and black-headed fall webworms closer to the equator have more flexibility in when they can breed, they may be able to avoid each other in time better, making speciation more effective.
Caterpillars in a lockdown
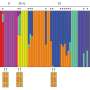
Thanks to the fall webworm's fluffy appearance and garden pest status, thousands of geotagged and dated photographs were available on the crowd-sourced science site iNaturalist. We reviewed 11,000 fall webworm photos from over 7,000 users, manually checking the thousands of photographs for whether the caterpillar was red- or black-headed.
While quite a feat, these methods gave us a window into fall webworm populations from Florida to Ontario. To see how speciation was changing across latitudes, we compiled the times and dates each fall webworm photograph was taken and measured the colors of the caterpillars from each picture.
Using all these observations, we found that in more northerly regions with short summers, the red-headed and black-headed fall webworm caterpillars were forced to breed at the same time and had more similar coloration. This suggests that more breeding was occurring between the groups, and they looked and acted more like a single species.
However, in their southern range, the black- and red-headed caterpillars were able to separate their generations more and had less similar coloration, meaning they may be further along in the process of becoming two species.
Climate and diversity
We found that differences in climate from the equator to the poles affect how well species can evolve when time is the barrier, mirroring the latitudinal biodiversity gradient. In short, climate can change how easily species form in the first place.
There are approximately 2.1 million classified species on Earth, and over one million of these are insects (with many millions more undiscovered), making them the most diverse animals on the planet.
Species are migrating, either as invasive species coming to new places, or moving poleward to escape warming climates.
Humans have an immense effect on our planet's ecosystems, and new species may be forming just as quickly as they disappear. So, to understand processes driving biodiversity on Earth, we need to understand how those processes impact the creatures that make up much of that biodiversity.
More information: Emily N. Black et al, Crowd-sourced observations of a polyphagous moth reveal evidence of allochronic speciation varying along a latitudinal gradient, PLOS ONE (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288415
Journal information: PLoS ONE
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()