This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Southwest Indian Ocean Ridge develops diverse hydrothermal systems, potential large polymetallic deposits
The research findings of Dr. Tao Chunhui, a senior researcher from the Second Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, were published in Science China Earth Sciences. Over a decade, Dr. Tao's research team conducted investigations into the distribution patterns and formation mechanisms of hydrothermal activities and associated polymetallic sulfides in the Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR).
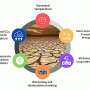
They discovered a diverse range of hydrothermal activities with higher frequency and the potential for forming large-scale sulfide mineral deposits than what expected by previous theoretical model. The team also established a sulfide metallogenic model controlled by local enhanced heat supply and deep faults (eHeat-dFault model).
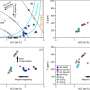
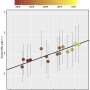
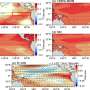
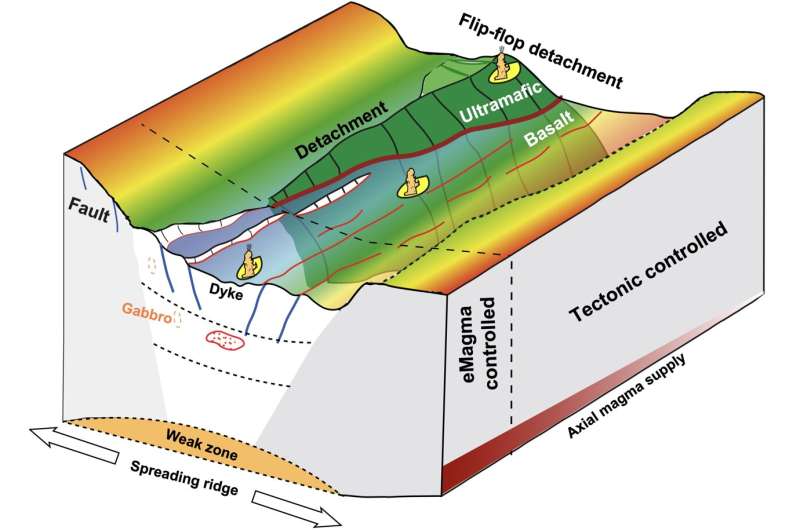
Submarine polymetallic sulfides have significant economic value and are primarily formed through hydrothermal circulation. The two key elements of hydrothermal circulation are the driving heat source and fluid circulation pathways. Through analysis of submarine seismic data, it was found that the driving heat source of the hydrothermal system in the SWIR exhibits local enhanced characteristics, and the depth of the heat source and circulation conduit structures are deeper compared to similar hydrothermal systems in other ridges.
These characteristics are mainly manifested in deep magma chambers in the strong magmatic segment, deep detachment faults in the weak magmatic segment, and flip-flop detachment faults in the amagmatic segment. It is commonly believed that the spreading rate controls heat source, magma supply, and tectonic processes.
However, this study suggests that the type of hydrothermal circulation system, circulation depth, frequency of hydrothermal activity along the axis, and the scale of sulfide mineralization may be the result of a balance between magma supply and tectonic activity.
For the ultraslow spreading SWIR, local enhanced heat supply and deep fault structures are more direct controlling factors for hydrothermal circulation and sulfide mineralization. The eHeat-dFault sulfide metallogenic model is expected to provide guidance for the exploration and mineralization research of polymetallic sulfides on the ultraslow spreading SWIR.
More information: Chunhui Tao et al, Sulfide metallogenic model for the ultraslow-spreading Southwest Indian Ridge, Science China Earth Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11430-023-1108-7
Journal information: Science China Earth Sciences
Provided by Science China Press