This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Researchers turn black bitumen into green carbon fibers

Bitumen, the sticky product from Alberta's oil sands, is normally burned as fuel or gets a second life as asphalt pavement.
But what if it could be turned into something more valuable, like the carbon fibers that make aircraft and hockey sticks light and durable, and electric cars safer and more efficient?
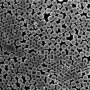
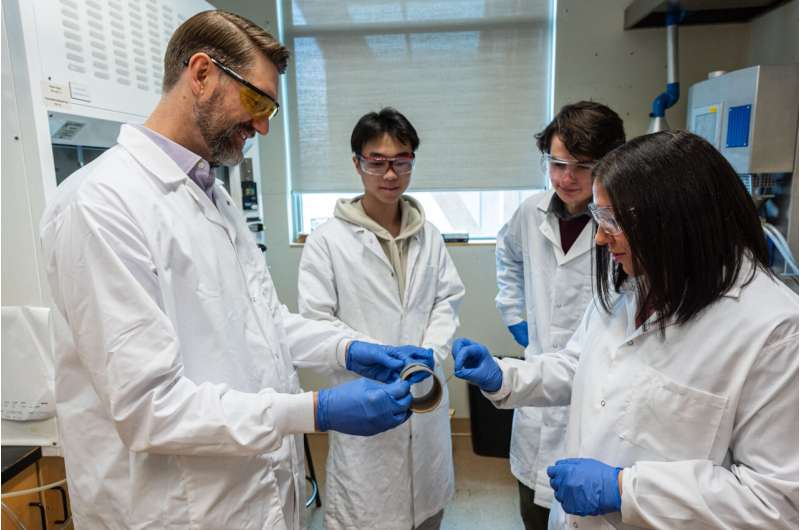
UBC materials engineer Dr. Yasmine Abdin and her colleagues, Dr. Frank Ko in the faculty of applied science and Dr. Scott Renneckar in the faculty of forestry, have developed a way to convert bitumen into commercial-grade carbon fibers.
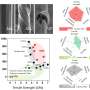
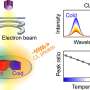
Their solution, described recently in the journal Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, uses melt spinning to produce two sizes of fibers cleanly and economically. Projected cost is $12 per kilo, compared to commercial carbon fibers that normally cost $33 per kilo.
The solution won the first two phases of the Carbon Fiber Grand Challenge, a competition launched by Alberta Innovates to recover valuable products from oil sands, and the team plans to apply for the third phase of the challenge.
Electric dreams
The team expects to start commercial production in 2024, and sees wide applications for their carbon fibers in electric cars, improving vehicle performance and ultimately helping to boost EV adoption rates.
"Carbon-fiber bodies can compensate for the weight of the typical EV battery pack. Using carbon fibers in the chassis helps the battery stay cool, improving safety and extending the driving range," says Dr. Abdin.
With around two million cars and other light vehicles being manufactured in Canada annually, she adds, using local carbon fibers can give automakers a competitive edge, while supporting Canada's goals for reducing emissions.
More information: Atif Hussain et al, Development of low-cost electrospun carbon nanofibers using asphaltene precursor, Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1088/2043-6262/acd6e7