This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New video series captures team working on NASA's Europa Clipper
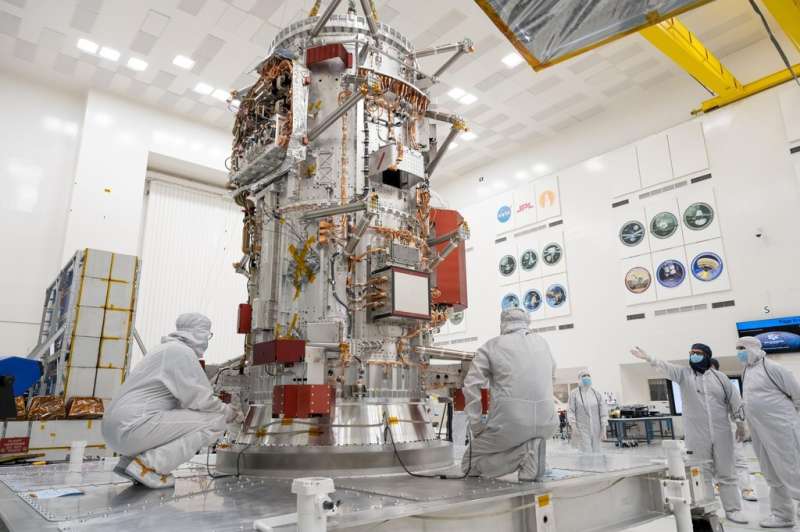

Destined for Jupiter's icy moon Europa, the Europa Clipper spacecraft—the largest NASA has ever flown on an interplanetary mission—is being readied to launch in October 2024. Between now and then, thousands of hours of work will go into assembling and testing the spacecraft to ensure it's hardy enough to survive a six-year 1.6-billion-mile (2.6 billion kilometer) journey and sophisticated enough to perform a detailed science investigation of this mysterious moon.
The new video series "Spacecraft Makers: Europa Clipper" offers quick updates on the mission's progress and lifts the curtain on the exacting work that goes into making sure the spacecraft reaches the Jupiter system in 2030. Europa Clipper aims to help answer questions about the ocean that scientists strongly believe lies below Europa's icy crust.
The spacecraft will fly by the moon about 50 times while orbiting Jupiter. (It can't orbit Europa because doing so would bring Europa Clipper too close to the gas giant's brutal radiation belts. Learn more in the video.) On each flyby, a suite of science instruments will gather data on the depth of the subsurface ocean, the thickness of the ice crust, and, potentially, the characteristics of any plumes that may be venting subsurface water into space. The goal is to find out whether Europa has the potential to support life.
The series' premiere episode features Europa Clipper Project Manager Jordan Evans, who also has worked on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover and the agency's Hubble Space Telescope. In the video, he joins Deputy Science Manager Trina Ray, who worked on NASA's Cassini and Galileo missions. They venture into JPL's storied High Bay 1 clean room, where Europa Clipper is under construction—and where all of NASA's Mars rovers, the twin Voyager spacecraft, and other historic spacecraft were assembled.
Provided by NASA