This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Lossless light: Revisiting Raman gain and amplification in a silicon photonic platform
Stars emit light that travels through empty space without significant attenuation. The visual signal is essentially lossless until detected. After many years and billions of kilometers, starlight-photons may eventually encounter the earth's atmosphere and be decoded as a speck in the night sky by some lucky person's retina and brain.
Light emitted by a pump laser may wish for the same journey lossless, but alas. For optical circuitry essential to computing and communication, light is sent through waveguides. In a silicon waveguide the light will attenuate after a few centimeters. With the right glass fiber (non-crystalline quartz silica, an oxide of silicon), photons can travel hundreds of kilometers before attenuation becomes too significant for information decoding.
So how does the trip across 9,000 km of trans-oceanic optical fiber communications work? Answer: Every ten kilometers, a section of fiber is loaded with erbium, a rare earth element, which acts to boost the traveling signal. (Oh, and lots of protective layers for the fiber because sharks are notorious for biting telecom/internet cabling. The exact reasons are unclear.)
You would think then we'd have the answer to signal amplification on a photonic integrated circuit (PIC). Chips are relatively small and the chance of a shark attack minimal. Alas, erbium-doped waveguide amplifiers had to be abandoned because their gain and output power could not match other amplifier technologies. Worse, their fabrication is incompatible with contemporary photonic integration manufacturing techniques.
So, the route to a lossless technology for PIC has remained an academic research topic for the last twenty years, even while "good enough" technologies are used for amplification/boosting of signals in today's chips and we put up with their needing lots of electricity.
For silicon-based PIC, non-linear photophysical properties have shown most promise. In essence, nonlinear effects enable manipulation of light by light. Being intrinsic properties, the implementation on non-linear behavior does not require special materials processing. It can be realized directly within in a standard waveguide with the right stimulation.
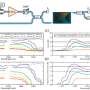
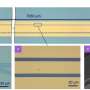
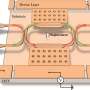
Enter the collaborative work between Canadian professors Shi and LaRochelle reported in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics: "Non-Reciprocal Sub-Micron Waveguide Raman Amplifiers, Towards Loss-Less Silicon Photonics." The team leverages new fabrication offerings from a foundry that manufactures PICs. The abilities of this foundry allowed the team to revisit Raman gain and amplification in a silicon photonic platform.
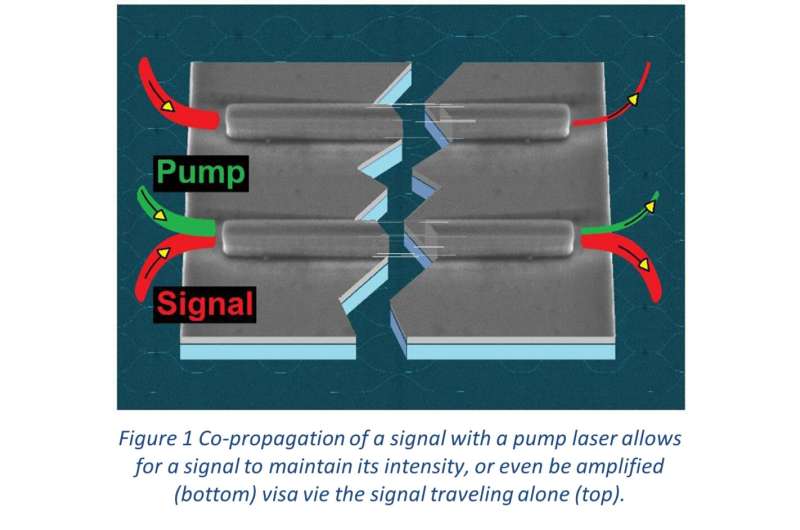
Raman scattering commonly transfers photon energy from a pump laser to vibration modes. It is known to spectroscopists looking for a materials specific signature. This energy transfer can boost the intensity of a signal at the energy resonant with the lattice vibration mode. The stimulated Raman emission in silicon becomes a powerful nonlinear effect, especially when the waveguide dimensions are shrunk down.
The co-propagation of a 20-100 mW pump laser allows for a signal to maintain its intensity, or even be amplified. Using the same waveguide dimensions configured into an optical resonator, the same team demonstrated efficient lasing covering an extended wavelength range around 1550 nm.
The battle to mitigate losses in a photonic circuit finds many angles. Like glass fiber engineering, materials with lower losses such as silicon nitride have been developed and are critical for applications where amplification is not an option, in quantum photonics for example. Hybrid materials combinations appear as possible avenues both for light modulation and amplification. Proposed solutions should be guided to some extent by its integration with established fabrication methods as well as clever modifications such as this team was able to exploit.
More information: Mohammad Ahmadi et al, Non-reciprocal sub-micron waveguide Raman amplifiers, towards loss-less silicon photonics, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics (2022). DOI: 10.1109/JSTQE.2022.3195950
Provided by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers