This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Team develops 2D ultrasound-responsive antibacterial nano-sheets to effectively address bone tissue infection
A research team led by Professor Kelvin Yeung Wai-kwok from the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, School of Clinical Medicine, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed) has invented a non-invasive and non-antibiotics technology to effectively reduce methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in bony tissue.
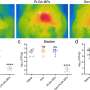
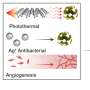
The novel antibacterial nano-sheets can release a substantial amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) subject to ultrasound stimulation. With the engulfment of neutrophil membrane (NM), the nano-sheets are able to actively capture the MRSA bacteria deeply seated in bony tissue and effectively eliminate 99.72% ± 0.03%. The research has been published in Advanced Materials.
Bone infection (osteomyelitis) is an infection in bone or bone marrow caused by bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms. The common causative pathogenic organism is MRSA. Severe infections can put patients at the risk of amputation, or even induce life-threatening sepsis. In clinical practice, the treatment of bone tissue infection typically involves antibiotics and surgical debridement to remove the infected bone or tissue.
However, excessive use of antibiotics not only compromises the host's innate immune function, but may also inevitably induce the emergence of drug-resistant pathogens. Recently, phototherapy (including photodynamic and photothermal therapy) has been applied as an antibiotic-free strategy to tackle bacterial infections. However, conventional phototherapy is unable to address deep tissue infection in bones due to its limited penetration power.
The researchers therefore pursued an alternative antibiotic-free strategy harnessing the penetration power of ultrasound in human tissues.
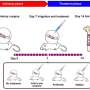
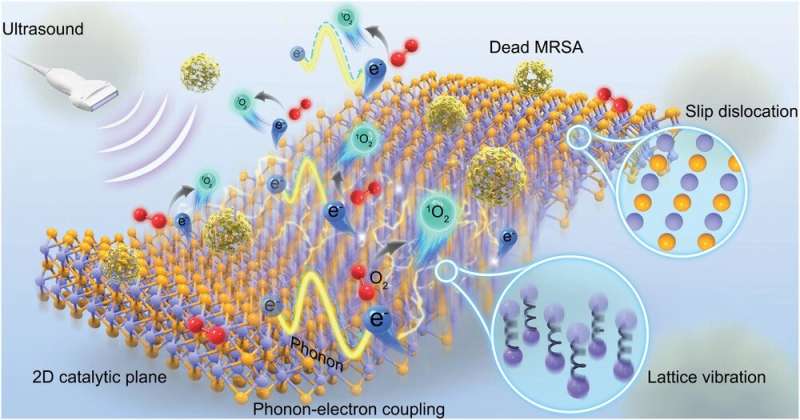
The HKUMed research team invented a new two-dimensional (2D) sonosensitizer, Ti3C2-SD(Ti3+) nano-sheets. A conventional sonosensitizer arranged in zero-dimension yields limited efficiency in ROS generation.
The innovative 2D sonosensitizer, containing an abundance of planar catalytic sites, can effectively generate a substantial amount of ROS when it is triggered by an ultrasound signal. After being covered with a neutrophil membrane (NM), the NM-Ti3C2-SD(Ti3+) nano-sheets (NM-nano-sheets) can actively track down the MRSA bacteria in bony tissue subject to ultrasound stimulation.
In an animal model, the novel nano-sheets have eliminated the MRSA bacteria in bone in more than 99.72% of cases, whereas the antibiotics therapy (Vanco) is ineffective. Furthermore, the NM-nano-sheets can also alleviate tissue inflammation and assist bone repair once bony tissue infection has been controlled. In addition, the NM-coated nano-sheets do not present any acute bio-safety issues.
Professor Kelvin Yeung Wai-kwok remarked, "Our design has achieved a qualitative leap in which the ROS catalytic site in sonosensitizer has transformed from zero-dimensional to two-dimensional. This invention can remarkably increase the production of bactericide (ROS). We may also consider applying this invention to the post-operation bacterial infection commonly seen in bone cancer patients or the patients with cystitis and peritonitis in the future."
More information: Congyang Mao et al, Realizing Highly Efficient Sonodynamic Bactericidal Capability through the Phonon–Electron Coupling Effect Using Two‐Dimensional Catalytic Planar Defects, Advanced Materials (2022). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202208681
Journal information: Advanced Materials
Provided by The University of Hong Kong