This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Neolithic ceramics reveal dairy processing from milk of multiple species
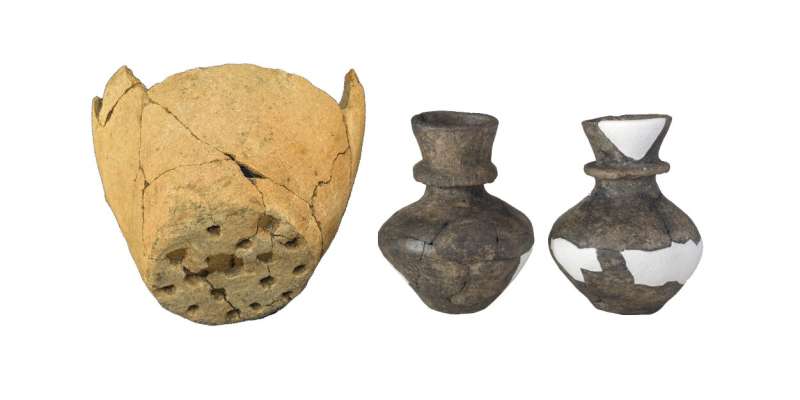

A new study has found evidence of cheesemaking, using milk from multiple animals, in Late Neolithic Poland.
The research suggests that early farmers reduced the lactose content in milk by making it into cheese or other dairy products like yogurt, and used dairy products from a number of different animals, such as cows, sheep or goats.
The study is published in the Royal Society Open Science.
Lactose intolerance was a common condition in almost everyone in Europe during the Neolithic Period and until the Late Bronze Age when a genetic mutation became widespread, enabling adults to produce lactase, the enzyme which breaks down lactose in the body.
Researchers looked at the practice of dairy processing in the Late Neolithic, identifying high curd-content residues in pottery indicating cheesemaking, and revealing that multiple dairy species were utilized.
Dr. Harry Robson, from the Department of Archaeology at the University of York, said, "These results contribute significantly to our understanding of the use of dairy products by some of the earliest farmers of Central Europe.
"Whilst previous research has shown that dairy products were widely available in some European regions during this period, here, for the first time, we have clear evidence for a diversified dairy herd, including cattle, sheep and goats, from the analysis of ceramics."
The scientists and archaeologists from the Universities of York, Cambridge, Toruń and Kraków used a multi-stranded proteomic and lipid-analysis approach to investigate ceramics and deposits on their surface, from the site of Sławęcinek in central Poland.
The new development provides evidence that cheesemaking (and other curd-enriching dairy processing) can be directly detected by scrutinizing the proportion of curd proteins, by comparing proteomic data. The results are also the first of their kind in Europe.
Despite widespread lactose intolerance in the period, there is evidence of dairy being consumed during the Neolithic, such as animal bones with kill patterns expected for dairy herds, dairy lipids in ceramic vessels, and dairy proteins in ancient dental calculus or plaque.
Lead author, Miranda Evans, Ph.D. student at Cambridge's Department of Archaeology, said, "The proteomic results showed that the ancient residues closely resembled both the modern cheesemaking residues and cheese itself and not whole milk. This reveals that the people of Sławęcinek practiced cheesemaking or another form of curd-enriching dairy processing."
Evidence of multiple species used for cheesemaking was backed up by the presence of both cow and sheep or goat bones on the site."
Dr. Jasmine Lundy from the Department of Archaeology, said, "This study highlights how complementary lipid and proteomic analyses are, particularly in understanding the use of the ceramic vessel over time. From this, for example, we could see that not only did some techniques waterproof or seal the ceramics but also what foods were being produced in them."
More information: Detection of dairy products from multiple taxa in Late Neolithic pottery from Poland: an integrated biomolecular approach, Royal Society Open Science (2023). DOI: 10.1098/rsos.230124. royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsos.230124
Journal information: Royal Society Open Science
Provided by University of York