This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Novel synthetic porphyrin as a dual antidote against fire gas poisoning
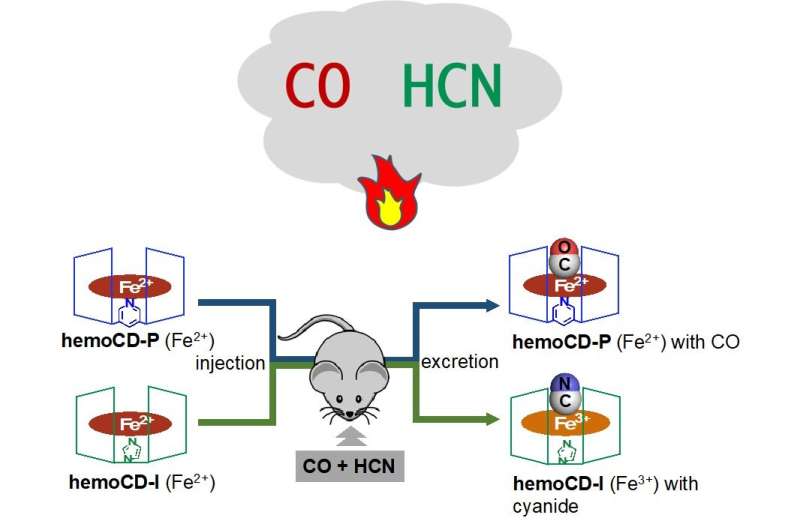
When buildings burn, the burning materials generate highly toxic carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) gases, which can be fatal upon ingestion. Once inhaled, these gases bind strongly to hemoglobin, cytochromes, and iron containing compounds known as hemes, and block normal aerobic respiration. It is believed that once an individual is exposed to these life-threatening toxins, it is impossible to effectively remove them from the body. In fact, at present, there is no therapeutic approach available to overcome simultaneous CO and HCN poisoning. This poses a significant challenge in saving lives of people exposed to toxic gases in building fires.
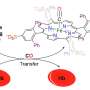
In a recent breakthrough, a team of researchers led by Professor Hiroaki Kitagishi from the Faculty of Science and Engineering, Doshisha University, Japan has developed a synthetic heme model compound termed hemoCD-Twins, that acts as an antidote for CO and HCN poisoning. In saline solution, hemoCD Twins dissolves into two heme models, of which hemoCD-P captures CO very strongly, and hemoCD-I effectively scavenges CN-.
Prof. Kitagishi and his collaborators—Dr. Qiyue Mao from Doshisha University, Dr. Xuansu Zhao from the Building Research Institute, Japan, Dr. Akiko Kiriyama from Doshisha Women's College of Liberal Arts, Japan, and Dr. Roberto Motterlini from University Paris Est Creteil, France—have detailed the development of this novel antidote in their recent research article published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
What was the motivation behind the development of this life-saving compound? Prof. Kitagishi says, "We have been studying synthetic heme-model compounds (hemoCDs) for over two decades. The series of hemoCDs, which comprises a mixture of synthetic organic compounds—porphyrin and cyclodextrins—has been our original heme-model system that realizes the biological functions of hemes using completely synthetic materials. One fine morning during the course of our research, I embarked on the idea that hemoCDs could be best used as antidotes against simultaneous poisoning by CO and HCN."
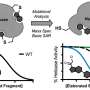
The team has also demonstrated hemoCD-Twins to be a very effective and rapid antidote against CO and HCN simultaneous poisoning in mice models. They found that in mice, this compound resulted in an 85% survival rate and rapid recovery. Moreover, this dual antidote exhibited very low toxicity and rapid elimination via urinary excretion. In addition, hemoCD-Twins had an immediate antidotal effect, a high degree of safety, and storage stability.
How will this antidote impact medicine in the long run? Prof. Kitagishi says, "This antidote will limit damage from gas poisoning caused by sudden fires and can be tested for the treatment of various symptoms caused by gas poisoning. With the completion of various non-clinical and clinical trials, within 5 to 10 years, we hope that hemoCD-Twins can be incorporated in ambulances, emergency hospitals and other facilities.
"This way, future generations will have no need to fear sudden fire gas poisoning. We will proceed with non-clinical and clinical trials in cooperation with medical doctors in order to implement this compound as a therapeutic agent in the world. For this purpose, we would like to request the cooperation from the general society."
More information: Mao, Qiyue et al, A synthetic porphyrin as an effective dual antidote against carbon monoxide and cyanide poisoning, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2209924120
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by Doshisha University