This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Neanderthals hunted, butchered massive elephants: study

Neanderthals may have lived in larger groups than previously believed, hunting massive elephants that were up to three times bigger than those of today, according to a new study.
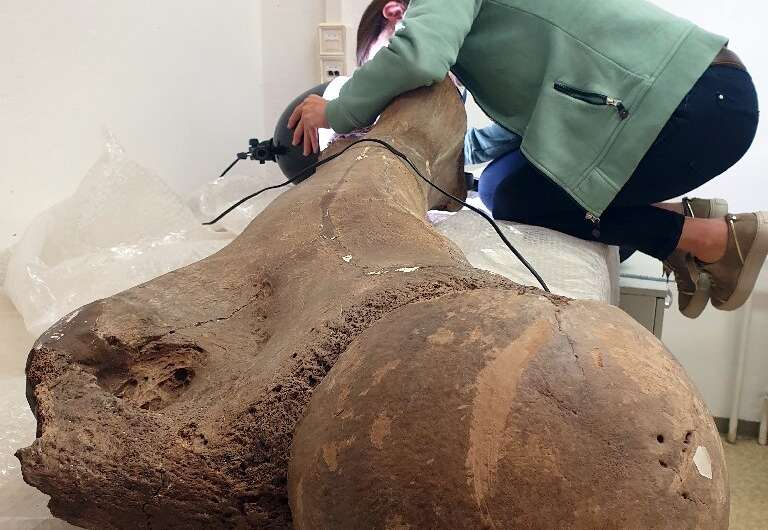
The researchers reached their conclusions, published in the journal Science Advances on Wednesday, based on examinations of the 125,000-year-old skeletal remains of straight-tusked elephants found near Halle in central Germany.
The bones of around 70 elephants from the Pleistocene era were discovered in the 1980s in a huge coal quarry that has since been converted into an artificial lake.
Elephants of the time were much larger than the woolly mammoth and three times the size of the present day Asian elephant, and an adult male could weigh up to 13 metric tons.
"Hunting these giant animals and completely butchering them was part of Neanderthal subsistence activities at this location," Wil Roebroeks, a co-author of the study, told AFP.
"This constitutes the first clear-cut evidence of elephant hunting in human evolution," said Roebroeks, a professor of archeology at Leiden University in the Netherlands.
The study suggests that the Neanderthals who lived in the area for 2,000 to 4,000 years were less mobile and formed social units "substantially larger than commonly envisaged."
"Neanderthals were not simple slaves of nature, original hippies living off the land," Roebroeks said.
"They were actually shaping their environment, by fire... and also by having a big impact on the biggest animals that were around in the world at that time."
'Calorie bombs'
The researchers determined the elephants had been hunted—and not just scavenged—because of the age and sex profile of the remains found in the quarry.
Most of them were males and there were few young or old ones.
"It's a typical selection made by hunters who went for the biggest prey," Roebroeks said.
Adult male elephants would have been easier to hunt than females, who tend to move in herds protecting their young.
"Whereas adult males are solitary animals most of the time," Roebroeks said. "So they are easier to immobilize, driving them into mud and pit traps.

"And they are the biggest calorie bombs that are walking around in these landscapes."
The researchers said the Neanderthals were able to preserve the huge quantities of food provided by a single elephant and it would sustain them for months.
"An average male elephant of about 10 tons would have yielded something like, minimally, 2,500 daily portions for an adult Neanderthal," Roebroeks said.
"They could deal with it, either by preserving it for longer time periods—that is already something that we didn't know—or simply by the fact that they lived in much, much larger groups than we commonly infer."
Cut marks
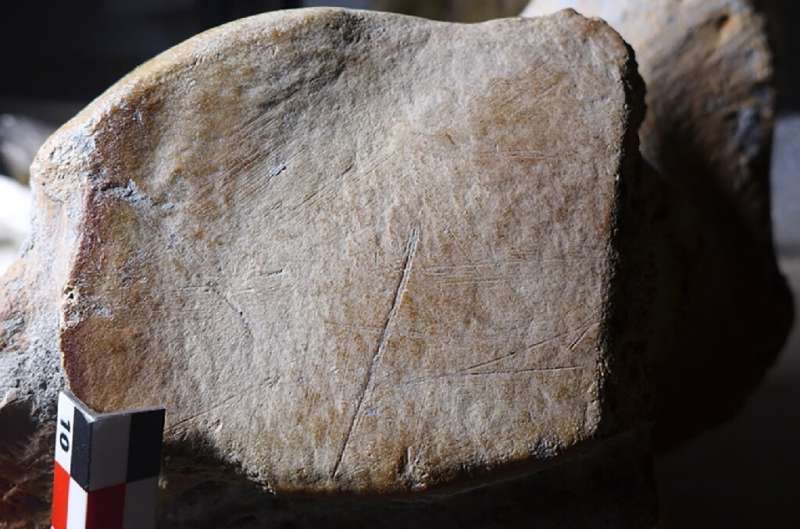
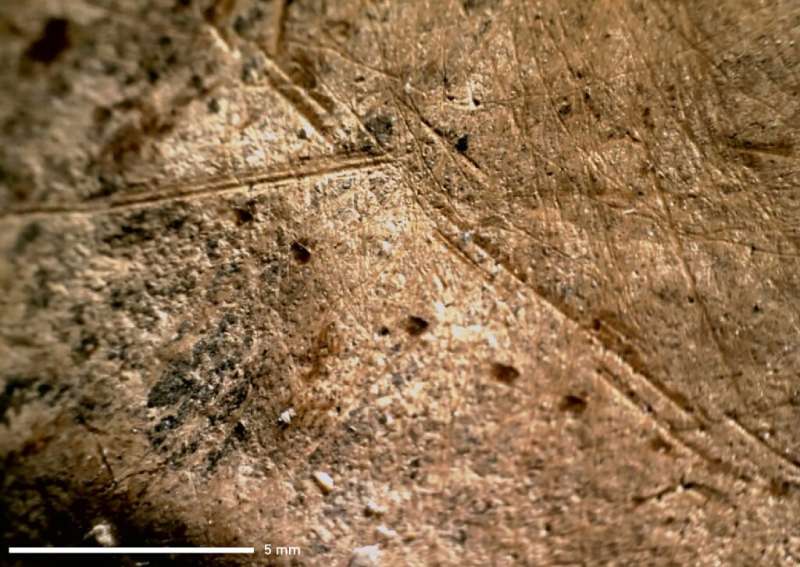
The researchers said the Neanderthals used flint tools to butcher the animals which left clear traces on the well preserved bones.
"They are classical cut marks that are generated by cutting and scraping off the meat from the bones," Roebroeks said.

Traces of charcoal fires used by the Neanderthals were also found, suggesting they may have dried meat by hanging it on racks and building a fire underneath.
Roebroeks said that while the study provides evidence the Neanderthals lived in large social units it is difficult to estimate exactly how large those groups actually were.
"But if you have a 10-ton elephant and you want to process that animal before it becomes rotten you need something like 20 people to finish it in a week," he said.
More information: Britt M. Starkovich, Perception versus reality: Implications of elephant hunting by Neanderthals, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6072
Sabine Gaudzinski-Windheuser et al, Hunting and processing of straight-tusked elephants 125.000 years ago: Implications for Neanderthal behavior, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add8186 , www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.add8186
Journal information: Science Advances
© 2023 AFP



















