This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Protecting high seas off Chile's coast depends on UN vote in New York
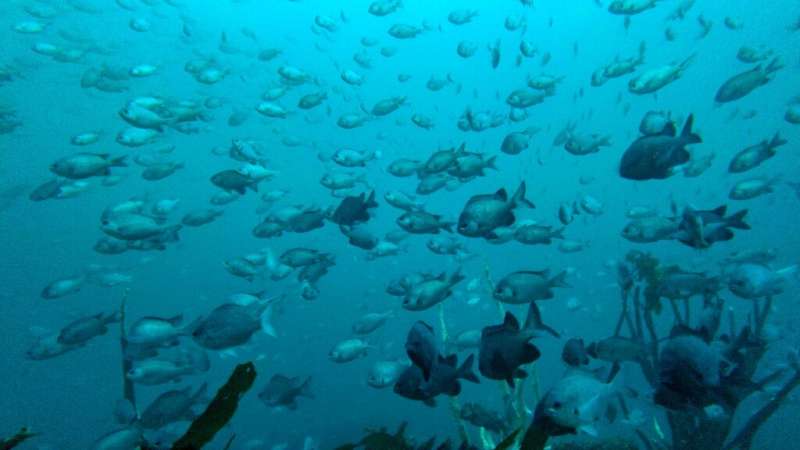

In international waters off the coasts of Chile and Peru, the ocean teems with plant and animal species—some do not exist anywhere else and many are endangered.
Urgently seeking to prevent biodiversity loss in these waters, Chile is pushing for a new marine protected area (MPA) to be created, and hoping to seal the deal during an upcoming summit at UN headquarters in New York.
With more than 6,400 kilometers (3,970 miles) of coastline, the South American country already has 42 MPAs covering some 150 million hectares or 43 percent of its exclusive economic zone, according to the environment ministry.
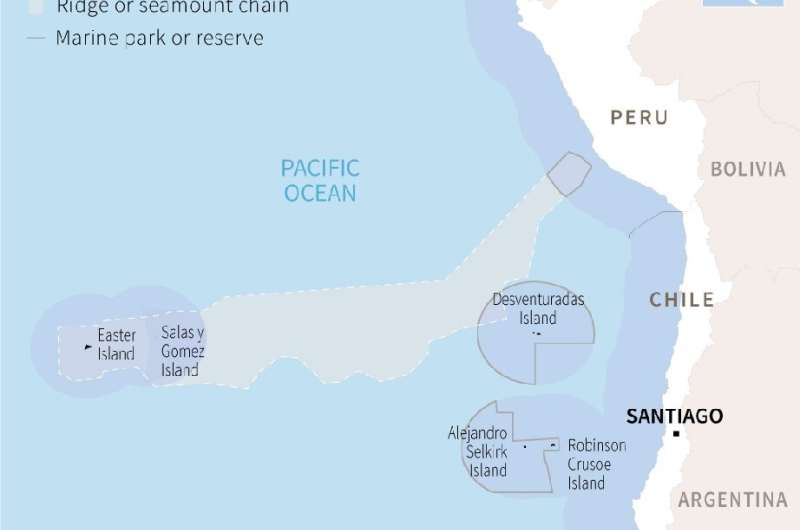
Now it is looking further afield: to international waters surrounding the Salas y Gomez and Nazca ridges—two seamount chains that flourish with biodiversity but are unprotected by law because they fall outside any national jurisdiction.
Those parts of the ridges that fall within Chile's exclusive economic zone or EEZ are already protected, as well as a portion that belongs to northern neighbor Peru.
But 70 percent of the ridges—two chains of more than 110 undersea mountains formed by volcanic activity that jointly stretch over 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles)—are not subject to any conservation or management measures.
It is home to whales, sea turtles, corals, sponges, starfish and a myriad of fish, molluscs and other crustaceans.
"Every time we go to that area and take samples, we find new species," Javier Sellanes, from the Center for Ecology and Sustainable Management of Oceanic Islands at the Catholic University of the North, told AFP.
'Unique diversity'
Sellanes, one of few Chilean researchers to have studied this remote area, describes the ridges as "a kind of oasis in the middle of a marine desert."
"Protecting that unique diversity on the planet is of high importance," he told AFP.
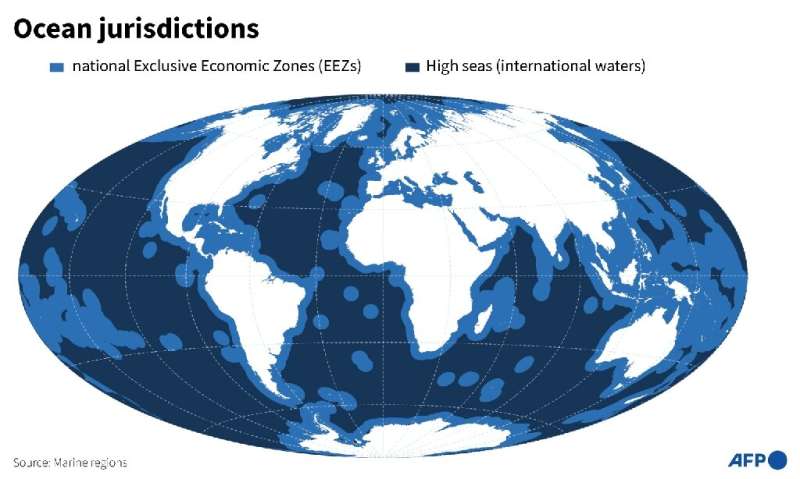
The high seas begin at the border of nations' EEZs, which under current international law stretch no more than 200 nautical miles (370 kilometers) from the coast.
Under no state's jurisdiction, the high seas cover nearly half the planet.
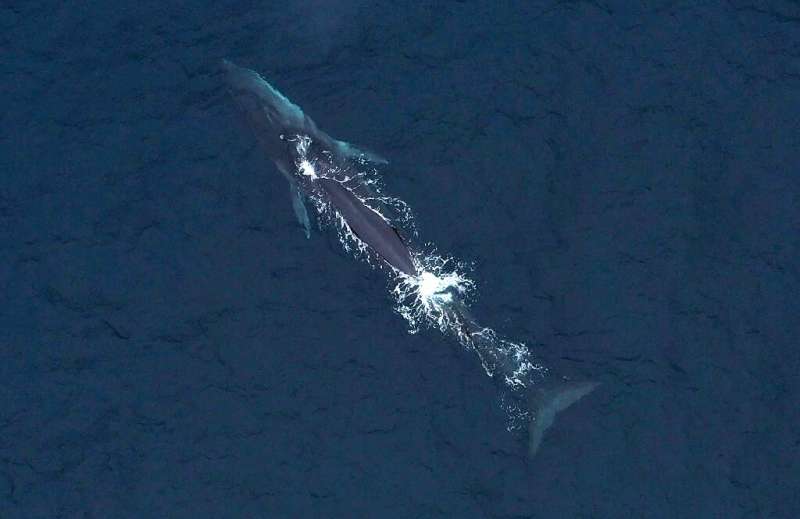

A 2021 study in the academic journal Marine Policy said the high seas areas of the Salas y Gomez and Nazca ridges are "under threat from a variety of stressors, including climate change, plastic pollution, overfishing, and potential deep-sea mining in the future."
As UN member states meet in New York next week in the hopes of finalizing a long-awaited treaty on high seas protection, Chile has already started work on having the area around the two ridges declared an MPA.
It could become the world's first, but time is of the essence.
"Importantly, fishing and other commercial activities are at low levels in international waters of this region, so there is a time-sensitive opportunity to protect its unique natural and cultural resources before they are degraded," the Marine Policy study said.
New UN High Seas Treaty
According to the High Seas Alliance of NGOs, the sea floor in this region contains cobalt and other highly-prized mineral deposits which could one day be targeted by deep sea mining.
"By permanently closing the area to fishing and mining and establishing a high seas MPA through a new UN High Seas Treaty, we can protect the Salas y Gomez and Nazca ridges for ourselves and for future generations," it states in an online report.
"While no contracts have yet been issued for exploration, neither are any of the areas officially closed to mining."
If adopted, the high seas treaty will allow UN members to propose the creation of MPAs for approval by majority vote. The document does not specify how protective measures will be financed or enforced.
As part of its campaign, Chile submitted a scientific report to the South Pacific Regional Fisheries Management Organization in 2021, in which it stressed that the benefits of the ocean, including food and climate stabilization, "are fundamental to life on Earth."
"The science is clear," read the presentation. "If the ocean is to remain sustainably productive, we must rebuild its health and urgently stop marine biodiversity loss."
© 2023 AFP