This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Glacier lakes swollen by global warming threaten millions
Violent flooding from glacier lakes formed or enlarged by climate change threatens at least 15 million people worldwide, most of them in four countries, researchers said Tuesday.
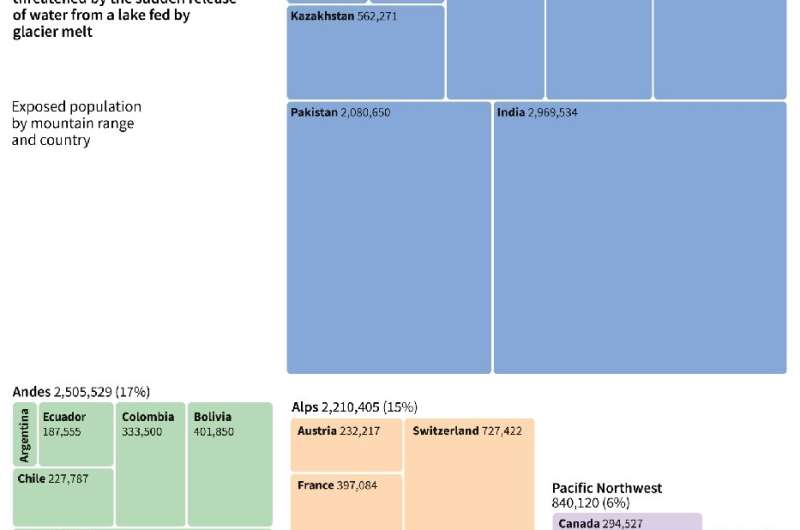
More than nine million people across so-called High Mountain Asia live in the path of potential glacial lake outburst floods, including five million in northern India and Pakistan, they reported in Nature Communications.
China and Peru are also especially exposed to the danger of abrupt flooding from melting glaciers, according to the study, the first global assessment of areas most at risk.
The volume of lakes formed as glaciers worldwide disintegrate due to global warming has jumped by 50 percent in 30 years, according to a 2020 study based on satellite data.
Earth's average surface temperature has risen nearly 1.2 degrees Celsius since preindustrial times, but high-mountain regions around the world have warmed at twice that pace.
Glacier lakes are particularly unstable because they are most often dammed by ice or sediment composed of loose rock and debris. When accumulating water bursts through these accidental barriers, massive flooding can occur downstream.
This kind of flooding has been responsible for thousands of deaths in the last century, as well as the destruction of communities, infrastructure and livestock.
"It's not the areas with the largest number or most rapidly growing lakes that are most dangerous," said lead author Caroline Taylor, a doctoral student at Newcastle University in England.
"Instead, it is the number of people, their proximity to a glacial lake, and, importantly, their ability to cope with a flood that determines the potential danger," she explained.
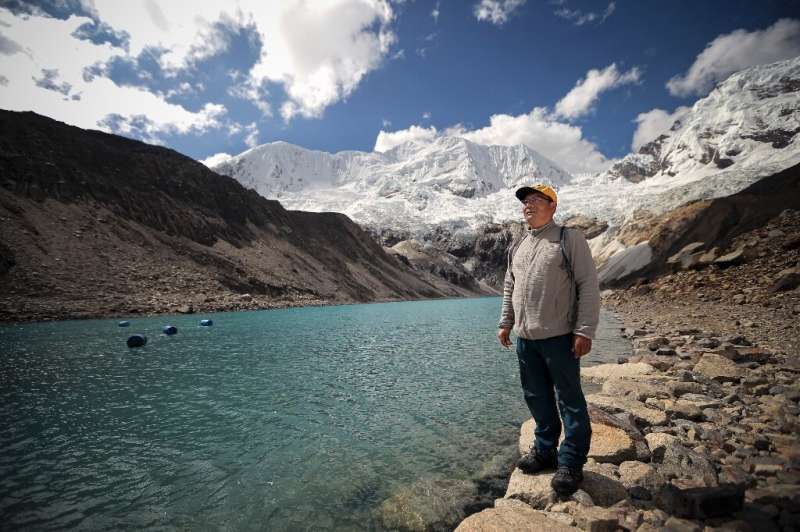

Thousands of people, for example, have been killed by glacier lake outburst floods in High Mountain Asia but only a handful in North America's Pacific Northwest, even though that region has twice as many glacial lakes.
To carry out the study, Taylor and her colleagues compared three sets of data: the number and condition of lakes fed by melt-water, the number of people living within 50 kilometers of a glacial lake basin, and how prepared communities are to cope with disaster should it arrive.
Some 90 million people across 30 countries live in 1,089 glacial lake basins, they found. 15 million of them reside within one kilometer of the track an outburst flood would take.
Exposure vs. vulnerability
Pakistan is home to more than 7,000 glaciers in the spectacular Himalaya, Hindu Kush and Karakoram mountain ranges, more than anywhere else on Earth outside the poles.
Last summer, on the heels of a two-month heat wave and during sustained rains that followed, raging torrents from melting glaciers in northern Pakistan ripped up thousands of kilometers of roads and railway tracks, destroyed bridges, and washed away entire villages.
In Peru, a 41-year-old farmer who lives in mountains near the city of Huaraz has filed suit against the German firm RWE, saying its greenhouse gas emissions are partly responsible for the melting of nearby glaciers.
Last year a delegation of German judges visited the region to determine what risk the expanding lake below the Palcacocha glacier poses to city of Huaraz and its 120,000 inhabitants.
Half of the Earth's 215,000 glaciers and a quarter of their mass will melt away by the end of the century even if global warming can be capped at 1.5 degrees Celsius, the ambitious Paris Agreement target that many scientists now say is beyond reach, a recent study found.
Over the past century, a third of global sea-level rises came from glacier melt, according to earlier research.
More information: Tom Robinson, Glacial lake outburst floods threaten millions globally, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36033-x. www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36033-x
Journal information: Nature Communications
© 2023 AFP