Researchers develop eco-friendly materials capable of purifying water
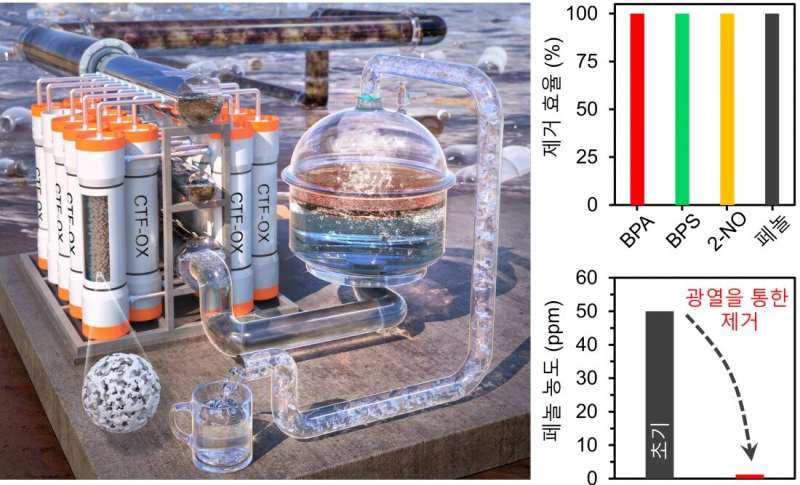
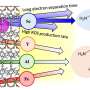
Professor Park Chi-Young's team successfully developed an atypical porous polymer material that can completely remove phenolic organic contaminants in water at ultra-high speeds. The porous material developed can efficiently remove not only microplastics in the water but also very small-sized volatile organic compounds (VOCs) based on photothermal effect. At the same time, it is expected to be utilized as a high-efficiency adsorption material that can be commercialized in the future as it has cost competitiveness based on raw materials and enables a solar-based water purification process.
Water pollution caused by the rapid development of the chemical industry is a pressing problem, and various water purification technologies and materials have been developed to address this issue. Carbon-based porous materials using existing adsorption mechanisms have limitations in that the adsorption rate is slow and high thermal energy is required for recycling. While various materials have been developed to improve contaminant removal efficiency, it has been difficult to develop materials that simultaneously satisfy excellent recyclability, high efficiency, economic efficiency of raw materials, and industrialization potential.
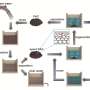
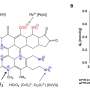
DGIST Department of Energy Science and Engineering Professor Park Chi-Young's team has now succeeded in synthesizing a porous polymer with excellent adsorption performance and photothermal properties by reacting an inexpensive and effective precursor. Also, an additional oxidation reaction was experimented on the polymer, and based on the results, a hydrophilic functional group was introduced to enable fast adsorption of micro-pollutants in the aquatic environment.
Furthermore, it was confirmed through experiments that the polymer developed by the research team does not require high thermal energy for recycling and can be used multiple times without loss of performance.
The research team produced a water treatment membrane capable of evaporating water using solar energy as a driving force through the developed polymer's ability to absorb light broadly and convert the absorbed light into heat. As a result, it was confirmed that the water treatment membrane coated with the oxidized polymer could purify phenolic contaminants through sunlight.
DGIST Department of Energy Science and Engineering Professor Park Chi-Young said, "The technology we developed here is an unrivaled water purification technology with the world's highest purification efficiency, removing more than 99.9% of phenolic microplastics and VOC contaminants in water at ultra-high speeds. We expected that it will be a universal technology with high economic efficiency that can purify contaminated water and supply drinking water even in areas where there is no power supply."
The research results were selected and published in Advanced Materials.
More information: Wansu Cho et al, Supramolecular Engineering of Amorphous Porous Polymers for Rapid Adsorption of Micropollutants and Solar‐Powered Volatile Organic Compounds Management, Advanced Materials (2022). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202206982
Journal information: Advanced Materials
Provided by Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST)