The missing link: Fatty acid metabolism impacts plant immunity
That healthy salad you ate for lunch contains fatty acids—surprised? Fatty acids, lipids, and fats in our food may sound undesirable, but they are foundational to human life and to the plants we consume. Their interaction with certain proteins helps regulate plant growth.
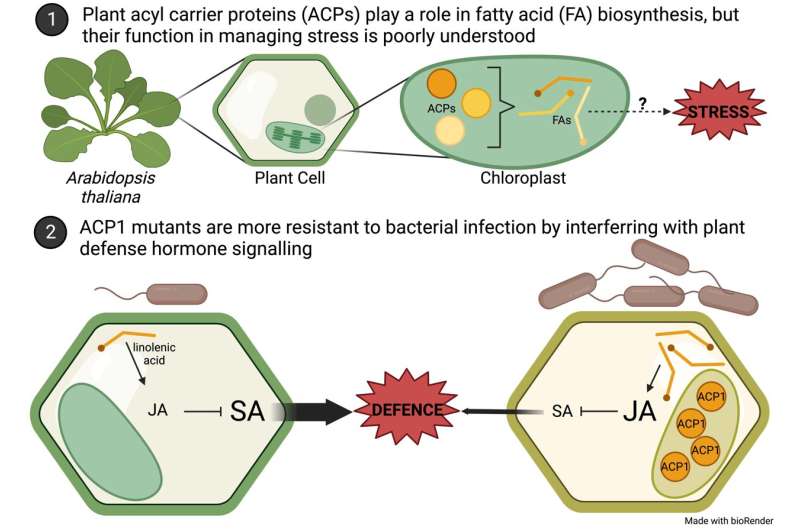
Plant fatty acids (FAs) serve as structural constituents of cell membranes and are building blocks for certain hormones, among other things. Fatty acids are stabilized during synthesis by acyl carrier proteins (ACPs), found throughout all branches of life, which support and elongate the growing FA chains. A recent study, by Zhenzhen Zhao of The Ohio State University and colleagues, reveals a new dimension to the role of FA biosynthesis in plants by providing a direct link to the plant defense mechanism.
Published in Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, the study found that the Arabidopsis plants lacking the Acyl Carrier Protein 1 (ACP1) were more resistant to the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae, indicating that FA metabolism plays a critical role in plant immunity. Corresponding author Ye Xia comments, "Our research provided a direct link between FA metabolism and plant immunity and unraveled the potential role of ACP1 in plant defense across economically important crops."

The study shows that ACP1 is essential to maintaining the homeostasis of hormones that affect a variety of plant stress responses. This effect on hormone signaling creates a broad arena for ACP1 to influence other biotic and abiotic stresses, an area ripe for further exploration. In addition, this research emphasizes the importance of studying individual members of gene families that may have discrete functions, since ACP1 plays a role in plant resistance—distinct from that of its close family member, ACP4.
ACP1 homologs are currently present in a variety of economically important crops. In the future, genetically engineering these important crops to modulate the expression of ACP1 is an exciting avenue to create disease-resistant varieties that withstand bacterial and other pathogen infections.
More information: Zhenzhen Zhao et al, Involvement of Arabidopsis Acyl Carrier Protein 1 in PAMP-Triggered Immunity, Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (2022). DOI: 10.1094/MPMI-02-22-0049-R
Journal information: Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions
Provided by American Phytopathological Society